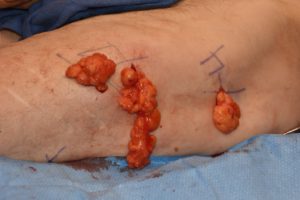
Lipomas are well known benign fatty tumors located in the subcutaneous tissues that are very common. Its hallmark is its encapsulation which both structurally identifies it as well as provides a method for its removal. Rather than making an incision that is equal to the diameter of the lipoma, its encapsulation provides a convenient method for its removal. The so-called small incision ‘squeeze’ techniques is well known and works for many lipomas particularly smaller ones. Larger lipomas are more problematic in this regard as they are adherently attached to the tissues.
In the April 2018 issue of the European Journal of Plastic Surgery, an article entitled ‘Subcutaneous lipomas: A minimally invasive method for resection of subcutaneous lipomas preserving retaining ligaments’. The authors describe a lipoma removal technique where through a small one inch incision, the lipomas were detached from the retaining ligaments bluntly with a finger. Tumors were then extracted either in a piecemeal fashion or with the squeeze technique. Complete lipoma resection was visually confirmed through the incisions.
In this paper the authors treated eighteen patients with an average size of over 6 cms. They were located in the shoulders, arms, back and thighs. Retaining ligaments were identified by MRI in all patients with the lipomas located between it and the periphery of the tumor. Larger lipomas greater than 10 cms proved no more difficult to extract than smaller ones with this removal method. No patient develop any complication such as chronic pain or residual numbness of the treated site.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapols Indiana


