As transgender plastic surgery becomes more prevalent, the number of patients seeking such face and body transformations are steadily increasing in number. In the male to female transgender patient, facial feminization surgeries and body enhancements of the breasts and buttocks are the mainstays of the physical metamorphosis.
In considering breast augmentation, there are initial obvious differences in the shape of the female vs. male chest. The absence of the development of a natural breast mound, the thickness of the pectoralis muscle and location/adherence of the inframammary fold are all considerations in how the phenotypic male chest will respond to the stretch of a breast implant.
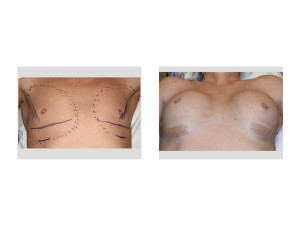
The pectoralis muscle is thicker in males and will thin to some degree with hormone therapies. The greater muscle thickness will contribute to increased upper pole fullness when the implant is placed in a partial submuscular or dual plane position and may be an accompanying reason with tighter skin that a rounder breast implant look often occurs. This can become even more evident or magnified when high profile saline implants are used.
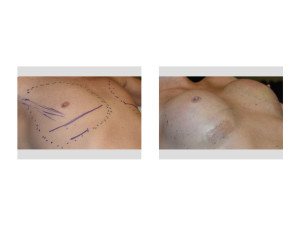
Transgender breast augmentation is a very successful procedure that creates a satisfactory breast mound despite some anatomic differences in the shape of genetically formed male chest.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana


