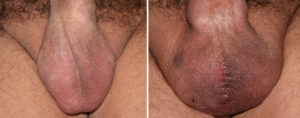
Background: The size of the normal male testicle is generally in the 3.5 to 4.5 cm range dependent on the overall size of the man. Certain conditions can cause the testicles to shrink or atrophy include aging, hormonal imbalance, and certain medical conditions. The effects of smaller testicles may become more apparent if the penis is enlarged creating a discrepancy in size between the penis and scrotum.
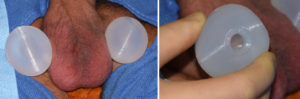
Increasing the size of the testicles can only be done with an implant. But this requires an implant design that is different than the traditional solid testicle implant. It requires a hollow implant to wrap around the testicle like a clamshell so to speak. But it must have an open end to allow the attached vascular pedicle of the testicle to remain unaffected.
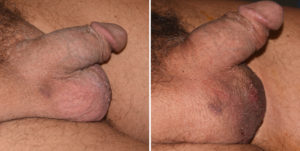
Case Highlights:
1) Enlarging one’s indwelling testicular size is done with a specially designed implant.
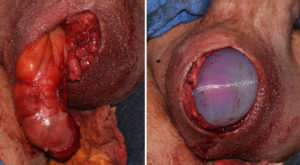
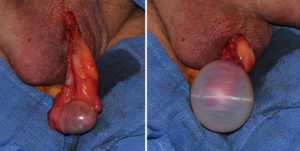
2) A testicular enlargement implant has a hollow center with an open end.
3) To place the testicle inside the implant it must be dissected out on its vascular pedicle which includes the vas deferens.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana