Background: The facelift procedure is an operation that is well known but not well appreciated by patients in its details. Much attention is given to various facelift techniques such as SMAS manipulation, deep plane dissection and cheek lifting. While all of these techniques are important and have valuable roles to play in facelift surgery, some of the most basic maneuvers in a facelift are often overlooked or downplayed.
While the lateral facelift work (SMAS flap and skin redrawing) has a hammock like effect on the central neck, which is an important effect, but the submentoplasty is what reshapes what lies under that skin pull.
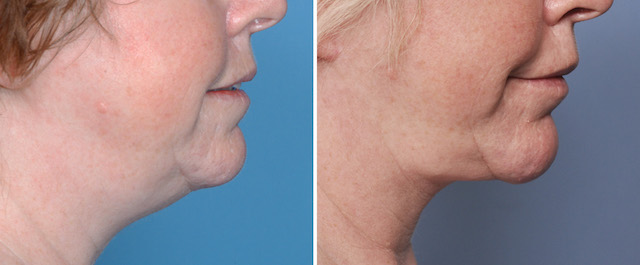
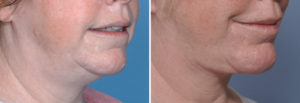
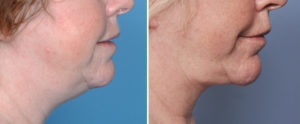
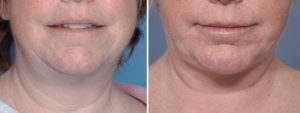
Case Study: This female desired to improve the shape of her lower face. She had thick facial and neck skin, an obtuse cervicomental angle and an indistinct jawline. She had adequate chin projection.
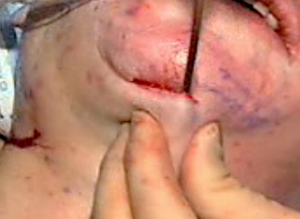
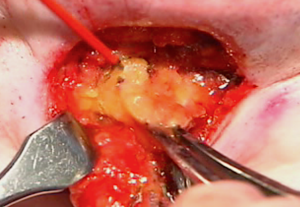
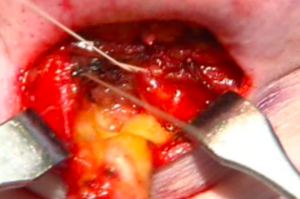
The submentoplasty part of the facelift has undergone innovations of late to get more profound neck changes. Deviating off of the midline in non-fat work other tissue excisions such as extended platysmal and anterior belly of the digastric muscle and submandibular gland removals can offer improved neck contouring in heavy or thick neck tissue patients. In thinner patients such neck tissue removals may over skeletonize the neck and should be considered with caution.
Case Highlights:
1) The submentoplasty part of a lower facelift is integral to obtaining an improved cervicomental angle.
2) The submentoplasty, done alone or as part of a facelift, involves liposuction, subplatysmal fat excision and platysma muscle modifications
3) The extended submentoplasty involves anterior digastric muscle excision, subtotal submandibular gland excision and platysmal muscle resection.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana