There are multiple techniques for browlifting surgery which differ by incision location and how the browlift is performed. (tissue excision vs tissue shifting) The endoscopic browlift technique is a tissue shifting method based on forehead skin and scalp relocation through subperiosteal mobilization and tissue fixation in an elevated and relocated position.While effective patients with a long/high forehead and significant forehead convexities/bossing are not ideal candidates as the endoscopic browlift will magnify those issues to some degree.
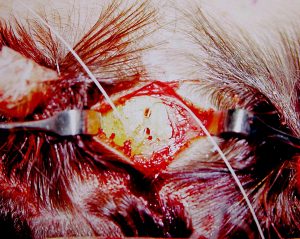
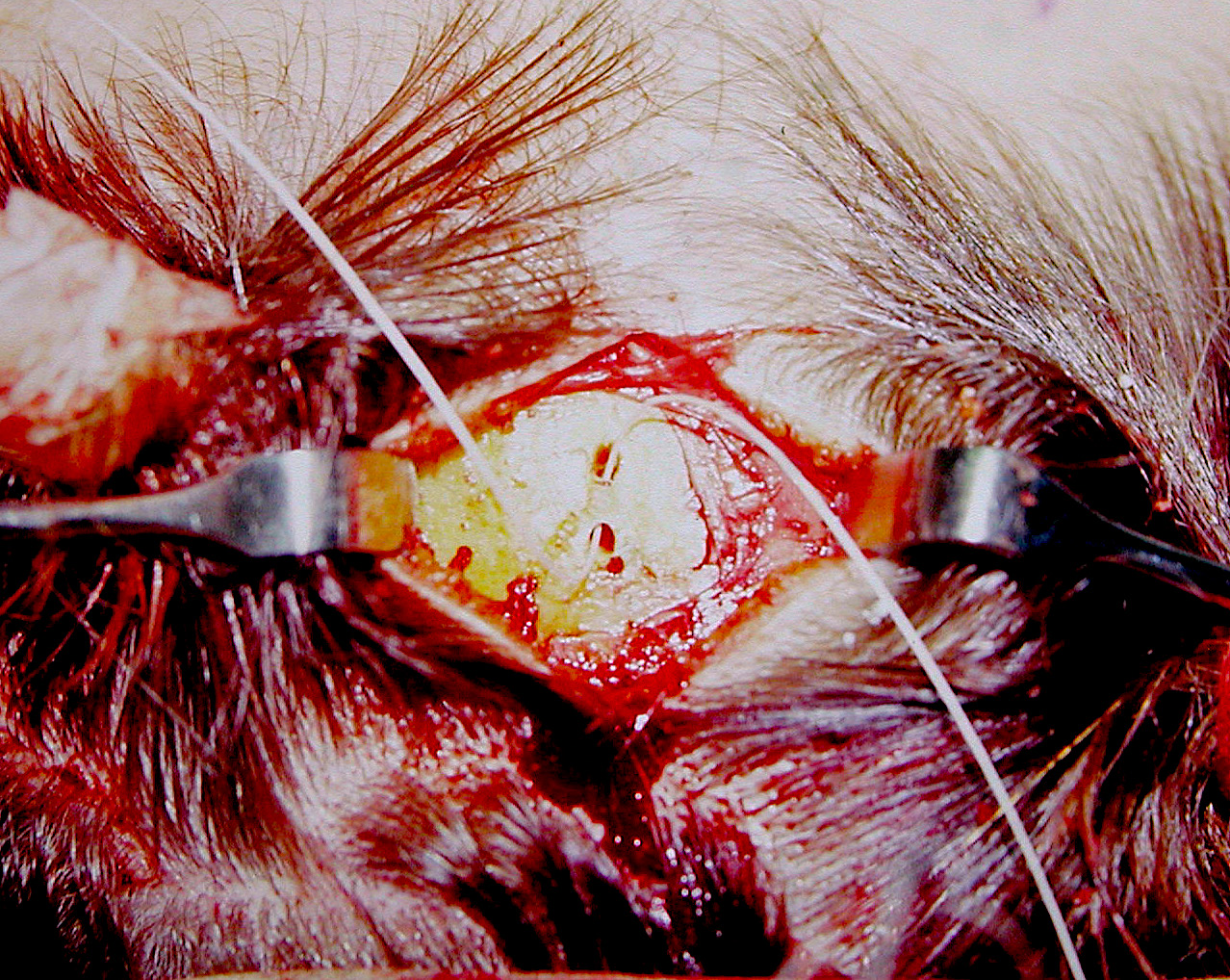
In the December 2021 issue of the Journal of Craniofacial Surgery an article was published on the topic entitled ‘Endoscopic Forehead Lift Using Pretrichial Vertical Incisions and Solid Suture Technique Effective Fixation and Lesser Scar Formation.’ The authors describe their experience with using pretrichial vertical scalp incisions with bone tunnel suture fixation in endoscopic browlifts in nearly 75 patients over a two year period. The scar results were assessed at 6 months using a rating scale based on surgeon and patient questionnaires. Most of the patients, not surprisingly, were women of middle age.
Sutures were removed one week after surgery. Follow up assessments were after six months. Scars were very thin and acceptable in most patients. Redness or suture track marks were not scar problems seen.
The authors conclude that retrichial vertical incision with cortical bone tunnel fixation using nonabsorbable suture provides several advantages comparing to conventional incision behind anterior hairline. Scar, which is the only potential concern, was not seen as a problem and can be overcome with the security of the bone tunnel fixation technique.
Dr Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana