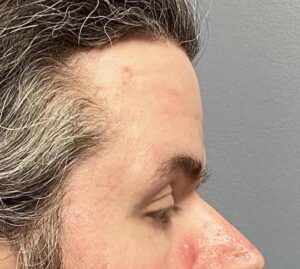
Background: The shape of the forehead in profile for both men and women has the upper forehead falling behind the projection of the brow bones. Because men have greater brow bone development than women they will have a greater backward slope to the forehead profile. But regardless of whether it is a male or female if the upper forehead projects further than the lower forehead this is known as frontal bossing and is an undesired aesthetic forehead shape.
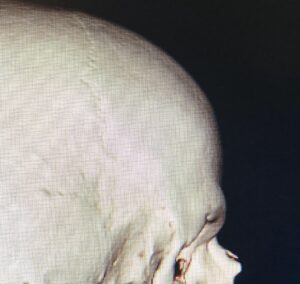
There are numerous causes of frontal bossing but I want to focus on the aesthetic type not those associated with syndromes or metabolic etiologies. In other words those cases that are less severe and have no known causes, so called idiopathic frontal bossing. It occurs in both men and women and is associated with specific skull shapes….meaning it rarely occurs in isolation. It is part of an overall skull development shape. The narrow skull shape in particular is often seen in frontal bossing. As the side to side width of the skull becomes less it pushes out in either the front, back or both. Less commonly it is seen in the wide skull shape where every aspect of the skull dimensions are bigger.
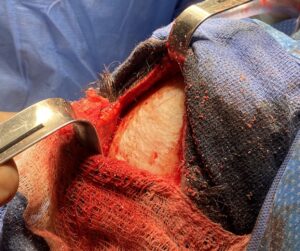
Frontal bossing can always be reduced, the only question is by how much. All of the skull’s five surfaces (fronts top, back and the two sides) the frontal bone is one of the thinner surfaces. And it usually doesn’t take more than 5mms until one is into the diploic space. But regardless of that general statement a preoperative 2D or 3D is needed to determine how much bone can be removed to determine the potential success of the procedure.
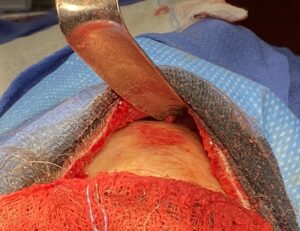

Case Highlights:
1) Frontal bossing is present when the upper forehead has more horizontal projection than that of the brow bones.
2) Frontal bossing is often associated with a more narrow skull shape.
3) The amount of frontal bossing reduction than can be achieved is controlled by the thickness of the frontal bone but usually enough reduction can be achieved to make a noticeable difference. (The projection falls behind that of the brow bones.
Dr. Barry Eppley
World-Renowned Plastic Surgeon