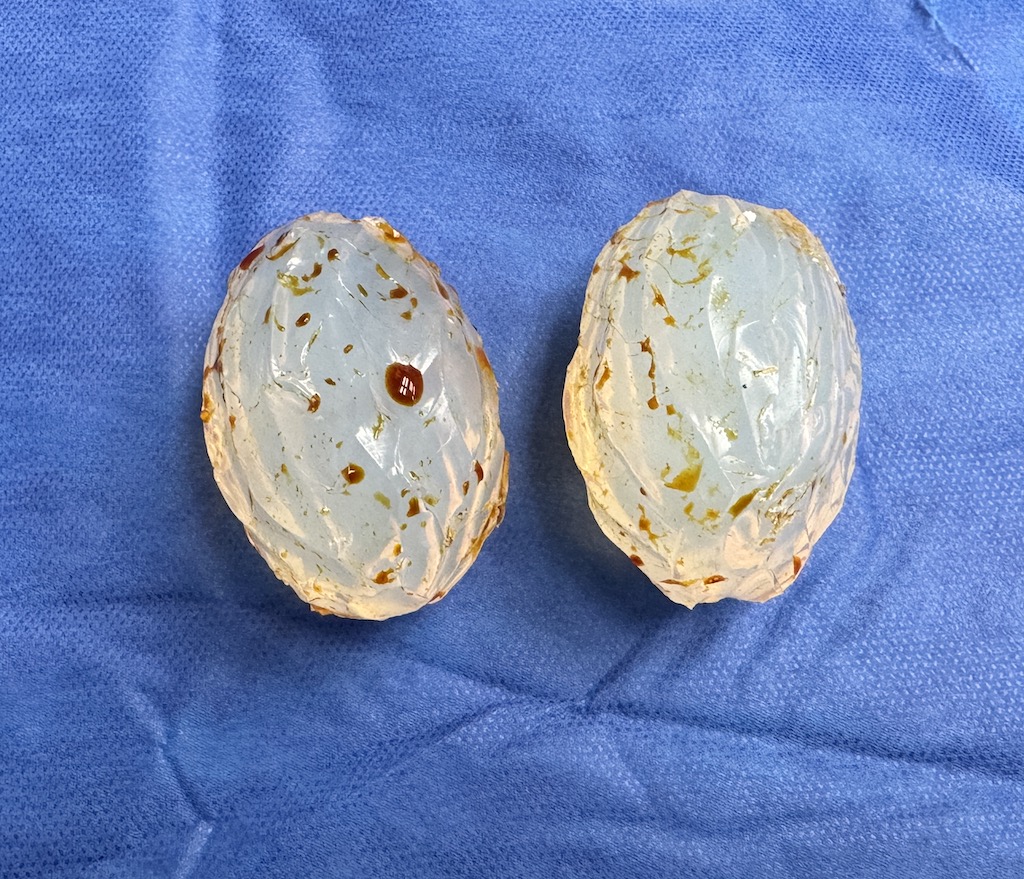
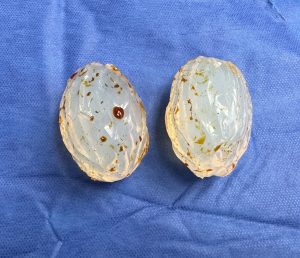
Background: The surgical treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED) is the penile prosthesis which has evolved over the years. While once just a stiff rod placed into the shaft penile prostheses today are more dynamic. Connected to a reservoir and a pump they can create erections on demand based on saline fill into the prosthesis. The reservoir is typically placed high and the pump low and accessible for activation. This places the pump in the scrotum which it is palpable and often visible as well.
While the placement of a penile prosthesis is an effective treatment of ED it can cause an aesthetic concern. The larger penis may make the scrotum look small or empty. (penile-scrotal disproportion) This can be exaggerated by natural testicles that have decreased in size due to aging and hormone supplementation. As a result this will have some men seeking testicle implants to improve the size and look of the scrotum.
The pump component of the penile prosthesis typically runs down the middle of the scrotum appearing as a bulge/bump at he bottom seen through the skin.This poses some challenges for testicle implant placement with a foreign body and its surrounding capsule occupying space inside the scrotum.

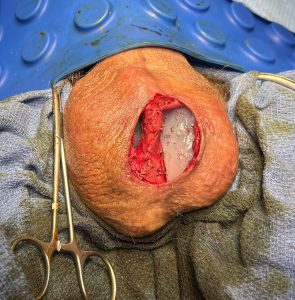
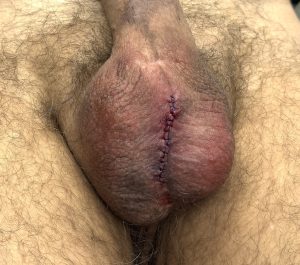
The scrotum is a small body area with not a lot of soft tissue in it. The combination of a penile pump and testicle implants creates a high implant load to tissue capacity which increases postoperative risks. To help mitigate these risks smaller implant sizes should be chosen.
Key Points:
1) The request for testicular enhancement is often seen in patients with erectile dysfunction in which a penile prosthesis may be present.
2) The presence of a midline using with a pump bulb down the center of the scrotum poses challenges and risks for placing custom testicle implants.
3) Given the risks of exposing and contaminating the penile prosthesis due to pump bulb location during the dissection the placement of custom testicle implants needs to the carefully considered and downsized if used.
Dr. Barry Eppley
World-Renowned Plastic Surgeon