Background: The hips, while occupying the side of the upper outer leg, have diverse areas of potential augmentation. Traditional hip augmentation typically refers to the soft tissue area below the iliac crest and extending down to or even beyond the greater trochanter of the femur. A variety of implants have been developed for this hip area with varying degrees of success. But aesthetically this approach is most effective when the upper hip area or the iliac crest has adequate width.
Iliac crest widths vary based on the genetic makeup of the bony pelvis. Females have a broader pelvis with more of an outward tilt to the ilium creating greater iliac crest width. Conversely males have less pelvic width as the ilium has a more superior angulation, raising the iliac crest higher but more narrow. As a result the concept of iliac crest upper hip augmentation has a role in two types of patients, the cis-female with a ‘boy-like’ pelvic width and the transfemale with a more naturally narrow pelvic width. This is the origin of the Pelvic Plasty procedure to increase the width of the iliac crest by the application of a titanium plate to its side.
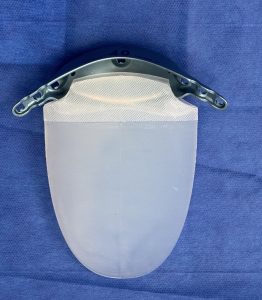
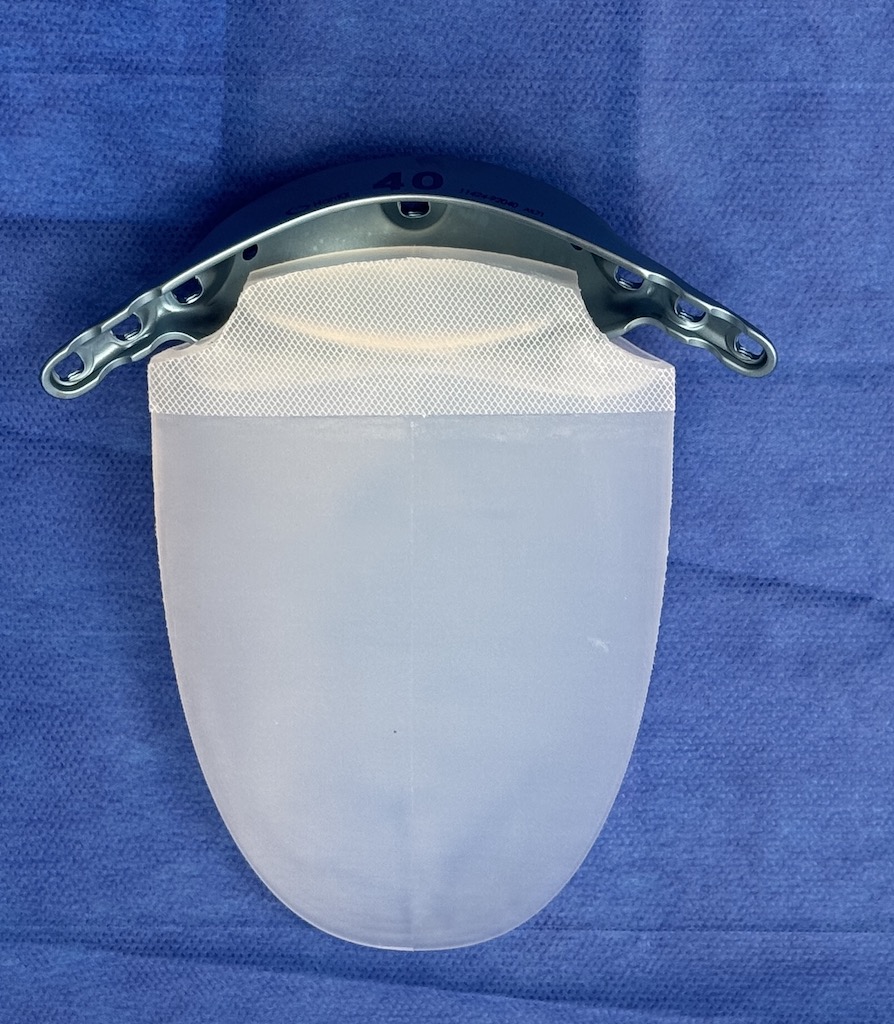
Case Study: This female patient desired skeletally-based hip augmentation with iliac plates. With her body type and thicker soft tissue layer a 40mm plate was chosen.

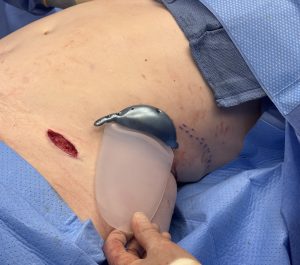
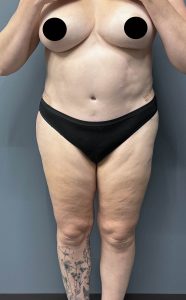
The incisions were closed with resorbable sutures over a drain on each side. The increased hip widening at the iliac crest area could be appreciated on the operative table.
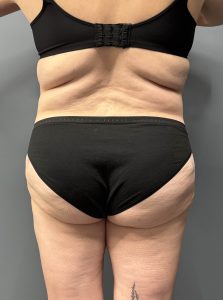
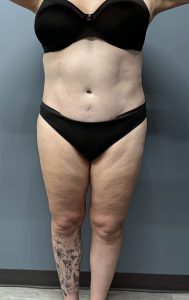
When seen days later for drain removal the improved iliac crest width could be seen without any subiliac hollowing. (back view)
Key Points
1) Pelvic Plasty is the augmentation of the iliac crest for upper hip widening for narrow bony hips.
2) In some patients iliac crest widening can create a subiliac hollow for which a hip implant has been designed to create a composite hard and and tissue hip augmentation effect.
3) Thicker tissue patients usually require wider iliac plates too ensure a visible augmentative effect.
Dr. Barry Eppley
World-Renowned Plastic Surgeon