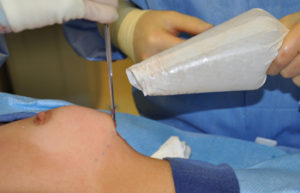
Background: Silicone breast implants can be inserted through various skin incisions because they are deformable. If they were not the size of the skin incision needed would have to be the same as the base diameter of the implant. In small breast implants this would be 11cm or 12 cms while larger breast implants could be as wide as 16 cms. Either way such incisional lengths would be unacceptable. Ideally incisional lengths for breast implants should be roughly one-fourth or 25% of its base diameter.
While the deformability of a silicone breast implant is important, how it is deformed for insertion is relevant. The traditional method is to use a ‘stuffing technique’ with one’s fingers on multiple areas of the implant’s shell. While eventually effective this creates permanent indentations on the implant’s shell which can potentially represent future fatigue points. Such shell fatigue points can result in disruption of its containment purpose, otherwise known as implant rupture. (not a term I prefer, it is better described as mechanical device failure)
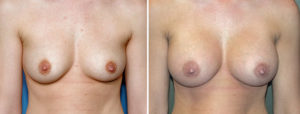
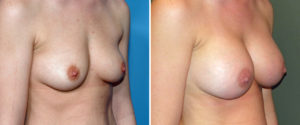
Case Study: This young female wanted to enhance her breasts from a small B to a small to medium C cup size. She opted for silicone implants at 300cc volume.
Highlights:
1) Breast implants are optimally inserted using a funnel technique to limit the risk of infection and improve the longevity of the implants.
2) Even small breast implants can be inserted with a funnel for the smallest inframammary incision possible.
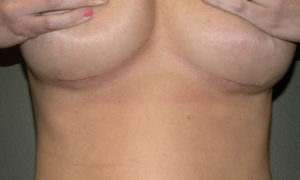
3) Silicone breast implants can be inserted through a small incision as 3 cms in length.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana