Background: Males almost always have much more pronounced brow bones than females due to a greater pneumatization effect of the frontal sinuses. Numerous studies have shown that the male frontal sinus is bigger, usually asymmetric and has a bigger left side than that of the right. This is clinically evident in the external shape of the forehead with greater supraorbital protrusions than females.
Why some men get much bigger and disproportionately larger frontal sinuses and subsequent brow bone protrusions is not known. Whether this is due to hormonal influence, masticatory loading forces or an increased developmental effort to separate the brain from the eyes are theories that have all been espoused. Regardless of its cause, the enlarged male brow bone often produces a dramatic effect that can be enhanced by a backward sloping forehead.
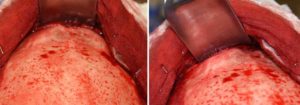
The male brow bone is reduced with several basic tenets in mind. First, simple burring is inadequate for a major brow bone protrusion. The anterior table of bone is not thick enough to allow for a significant reduction and the maintenance of a bony covering of the frontal sinus air cavity. Second, the male brow bone should be so reduced that the foreflat has a completely flat profile. Some degree of brow bone break into the upper forehead needs to be maintained.
Case Study: This 30 year-old male had been bothered for a long time by the shape of his forehead. He had a very strong brow bone with two very distinct paired brow protrusions with a midline glabellar groove. The size of the brow bones was magnified by a backward forehead inclination of almost 45 degrees.
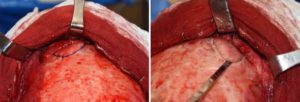
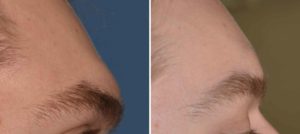
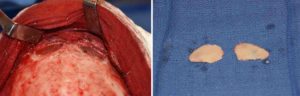
The osteoplastic setback technique for male brow bone reduction is the gold standard by which it is done. Whether it can be done by a single piece of bone across the frontal sinuses or whether it needs to be done by two separate bone pieces depends on the patient’s anatomy.
Highlights:
- Most brow bone reductions in men require an osteoplastic setback technique.
- Removing the anterior table of bone from the frontal sinus by osteotomy with surrounding burring produces the best brow bone reduction effect.
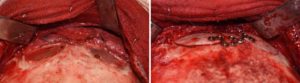
- Male brow bones should be only reduced to the point of leaving some brow bone break to avoid overfeminization of the forehead.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana