Background: Significant or extreme weight loss is defined as any amount over 75 lbs. or more. Such amounts of weight loss are most commonly caused by bariatric bypass, sleeve and gastric stapling procedures. Although there are some patients who do lose such large amounts of weight by their own diet and exercise efforts.
One of the well known effects of extreme amounts of weight loss is generalized tissue deflation and sagging skin. Depending on how much weight loss, gender and body location, there can be variable amounts of tissue thinning and loose skin. In general more sagging skin often occurs in women from the arms to the thighs than occurs in men. Part of this is due to better skin retractibility in men and having tissues that have never been previously stretched from pregnancies.
One body area where this gender difference in weight loss effects can be seen is the female breast and the male chest. In the female breast, which has an initial mound of tissue, volume deflation results in variable degrees of breast sagging over the inframammary fold. In the male chest, however, which may not have started out with a significant breast mound (although some men do have a large amount of breast tissue before the weight loss) the sagging of skin is usually less severe or may not be present at all.
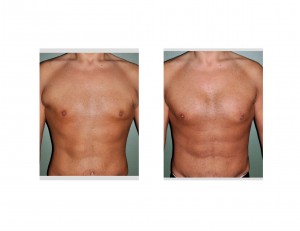
Case Study: This 35 year-old male lost almost 90lbs through his own diet and exercise efforts. He had become so focused through this process that he became extremely fit and focused on optimal body shape and contour. While he was at a very good weight and was as lean as he wanted, he was not able to build up his chest as much as he liked. He also had some extra skin under his armpits that created an unaesthetic bulge.
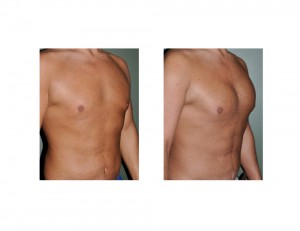
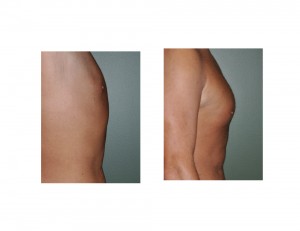
Chest reshaping in men who have lost a lot of weight requires a combination of muscle augmentation, the creation of muscular outlines by liposuction and the removal of any redundant axillary skin folds. While the residual tissue effects from weight loss do not affect the male chest as much as the female breast, a pectoral implant alone can not create a complete chest reshaping.
Case Highlights:
1) Significant weight loss can cause a generalized chest ‘deflation’ with loose skin
2) Pectoral implants can serve as the foundation for chest reshaping efforts after weight loss.
3) Soft tissue contouring around pectoral implants is needed in the weight patient to optimize the improvement in muscle definition.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana