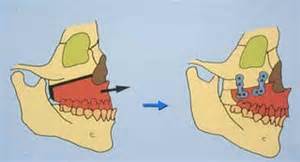
Background: Treatment of a midface deficiency is most commonly done by moving the upper jaw forward. Done by making a horizontal bone cut just above the roots of the teeth, the upper jaw is brought forward into a new horizontal position. This well known facial bone procedure is the LeFort I osteotomy and has been the backbone of everyday orthognathic surgery for the past fifty years.
But not every patient who is in need of a Lefort I osteotomy, or any form of orthognathic surgery, is always a good candidate for orthodontic therapy. Due to compliance issues or the inability to tolerate the intraoral manipulations of orthodontic appliances, consideration can be given to doing the surgery ‘braces free’. This is done with the understanding that the goal of an ideal occlusal interdigitation is not achievable.
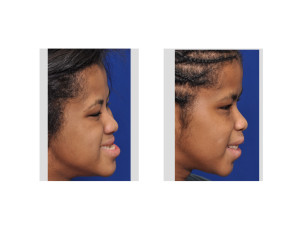
Case Study: This 15 year-old teenage female had a severe midface deficiency and upper airway obstruction due to a limited nasal airway. Due to a developmental delay, the application of orthodontic appliances and therapy was not possible.
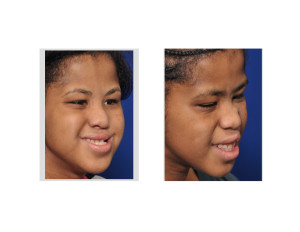
While any form of orthognathic surgery (maxillomandibular osteotomies) is ultimately judged by a specific measurable outcome (the occlusion), there are other facial benefits that can supercede how the teeth interdigitate…particularly when they do to fit that well initially anyway.
Highlights:
1) A maxillary advancement (LeFort I osteotomy) can be done in rare circumstances without the need for presurgical orthodontics.
2) A LeFort I osteotomy produces well known midface aesthetic benefits including profile enhancement and improved nasal airway breathing.
3) A non-orthodontic LeFort I advancement is a skeletal improvement procedure, not a dental one.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana