Background: Chin reduction is a procedure that is largely done in females. While a larger chin is often tolerated in a man, it is much less aesthetically pleasing in a female. It is the converse of a small chin which is far more tolerated in women than in men.
While chin reduction is done in women of all ages, the reasons may be somewhat different in older women than in those younger. Younger females with large chins are usually bothered by it from the time they have grown past puberty. It is a developmental issue and a basic facial reshaping concern. Conversely in some older women it is an issue that bas become magnified with aging. Loss of dentoalveolar support and facial tissue sagging can highlight a somewhat larger chin with a ptotic chin appearance. (witch’s chin)
Of the two basic chin reduction approaches, the submental approach is the most versatile. Its versatility comes from being able to manage soft tissue excess at the same time as that of a bony reduction. This is the one feature that primarily separates it from the intraoral chin reduction approach. It is also a but more facile.
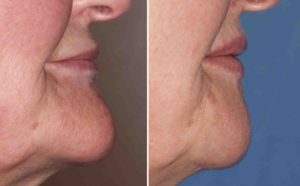
Case Study: This 63 year-old female was bothered by her large chin. The dimension that bothered her the most was its excessive horizontal projection as the pogonion (most anterior point of the chin) point was far ahead of lower lip projection.
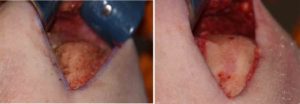
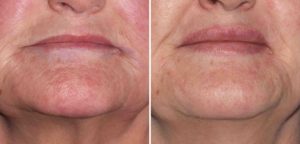
The proper name for an under the chin approach should be called ‘Chin Reduction with a Submental Tuck’ as this accurately what is actually done. For the older female a dual bony and soft tissue reductive technique is usually what is needed.
Case Highlights:
1) Chin reduction is often best performed through a submental skin incision.
2) A submental approach allows any redundant soft tissue chin pad tissue to be treated to prevent postoperative ptosis.
3) Chin reduction in older females is a particular indication for an external submental technique.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana