Background: Buttock implants are the lone remaining option after fat injections for buttock augmentation. If one has enough fat, or even if it may be marginal, I advise patients to pursue autologous fat injections first because it is both natural and has not long-term side effects from the graft itself. But some patients are too thin for fat harvesting to be an option or have failed prior fat grafting procedures due to graft absorption and are out of adequate fat donor sites.
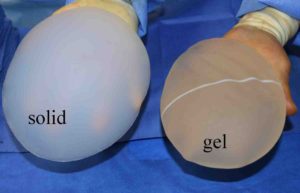
Buttock implants offer a permanent albeit invasive approach to buttock augmentation. Unlike breast implants, buttock implants in the United States are solid silicone and not a gel inside a surrounding silicone shell. As a result they are permanent implants that can not rupture or undergo implant failure once implanted for the duration of the patient’s lifetime.
But in may countries outside of the United States, the buttock implants used are gel devices. In removing and replacing numerous buttock implants placed outside the United States I have seen few breast implants used as well as gel implants that appear to be made for the buttocks. While this may seem incredulous there are actually good reasons why gel implants are used for the buttocks. They actually are a bit softer solid implants and are easier to place, particularly in the intramuscular location, due to their greater deformability. Their downside, like breast implants, is that they can rupture and that risk may be higher in an anatomic position exposed to the stresses of sitting.
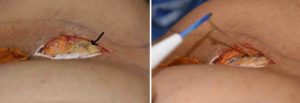
Case Study: This man wanted to replace his existing 500cc buttock implants, that were placed in Mexico, with new custom 700cc implants. He had no problems or pain with his existing implants he just wanted a larger size.
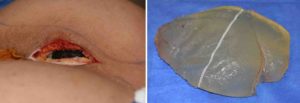
The new custom 700cc solid buttock implants were then inserted after cleaning out and irrigating out the partial intramuscular pockets.
Highlights:
1) Gel buttock implants have the potential for rupture and should not be considered lifelong devices.
2) Solid silicone buttock implants are permanent lifelong devices that will not rupture or fail.
3) Ruptured gel buttock implants can be successfully removed and replaced without adverse medical effects.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana