Background: The nose by virtue of its central facial position and protruding structure is frequently exposed to traumatic injury. Its fixed osteocartilaginous structure can become displaced when enough force is applied. The type of nasal injury depends on the direction and amount of force to which it is exposed.
Injuries that strike the nose directly in a straight on fashion can produce an impaction type nasal displacement. The central supporting septum, which acts like a tentpole, is pushed inward as the septum fractures as a result. With it other structures are drawn inward which could include the upper lateral cartilages, nasal bones or both. This type of traumatic nasal injury creates externally a saddle nose deformity due to a now concave dorsal profile. Internally the telescoped septum is deviated and may cause airway obstruction.
Reconstruction of the traumatic saddle nose deformity typically focuses on septal straightening/rearrangement and the re-establishment of septal height. This is what is done in a primary procedure. This may or may not adequately restore the dorsal line. If not then secondary reconstruction is needed which typically involves cartilage grafting.
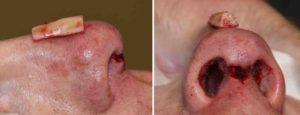
Case Study: This young male sustained a direct impact injury to his nose when falling forward onto the edge of a desk. This created a dent behind the tip of his nose with difficulty breathing though the left side. His septal fractures were initially treated by an ENT surgeon which restored his breathing but he remained with an indented dorsal profile right behind his nasal tip.
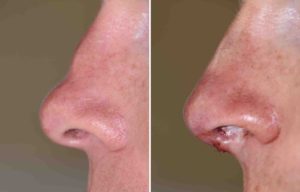
Small rib cartilage grafts can be an effective method in the treatment of the saddle nose deformity.
Case Highlights:
1) Traumatic saddle nose deformities typically involve loss of septal height and cartilage support.
2) Cartilage is the ideal material to reconstruct the dorsal height/line in the saddle nose deformity.
3) A rib graft of varying size always provides adequate cartilage material in rhinoplasty.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana