Background: Excessive chin projection can occur in numerous dimensions and often involves multiple dimensional excesses concurrently. But isolated chin excesses or single dimensional macrogenias (large chins) do occur and presents as either in the horizontal or vertical dimensions.
Vertical macrogenia can be effectively treated through two different approaches unlike many other types of large chins. An intraoral chin down fracture with a wedge ostectomy can shorten the height of the chin when the down fractured segment is brought back together. Conversely an inferior or submental technique can be done where the osteotomy is done from the inferior border rather than in the middle of the chin as in the intraoral approach. Both vertical chin reduction techniques have their advantages and disadvantages.
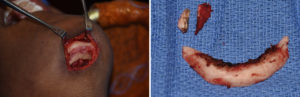
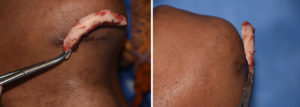
The submental chin reduction approach, because of the skin incision that is needed, often is thought of as not ideal. But it has several advantages including bone work that is well below the mental nerve and direct line of sight to remove and reshape the bone.
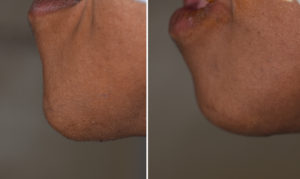
Case Study: This young female was bothered by her large chin which gave her face an excessively long appearance. By facial third measurements her lower facial third was out of proportion to the upper and middle facial thirds by a positive 15mms. (55mm upper, 55mm middle, 70mms lower third)
Highlights:
1) Chin reduction for excess vertical length can be done either through a submental or intraoral approach.
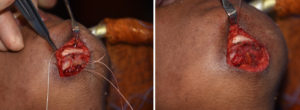
2) A submental approach for vertical chin reduction involves an inferior border removal, side shaving and geniohyoid muscle resuspension.
3) Submental vertical chin reduction may or may not require a soft tissue excision/tuck as well.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana