Background: Some of the earliest signs of facial aging affect the eye area. The frequent sphincteric closure of the eyes and their thin skin ensures that aging will appear first on one’s face. One of the inevitable eye changes is the development of extra skin on the upper eyelid. Due to the constant opening and closing of the upper eyelid, which moves a lot more than the lower eyelid, the development of stretched out skin is inevitable.
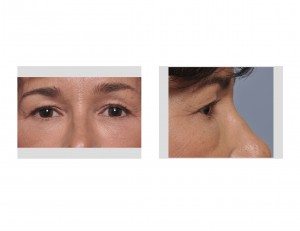
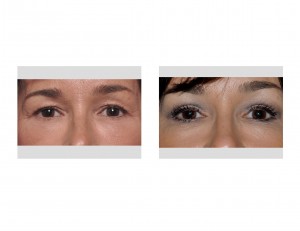
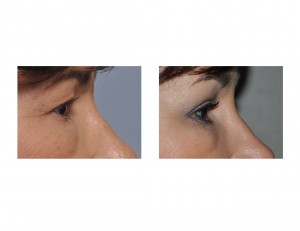
When it becomes significant enough, the extra skin will hang over the natural crease of the eyelid and eventually can hang down onto the lash line. This is known as upper eyelid hooding. The removal of this hooded upper eyelid skin is the primary objective of upper eyelid blepharoplasty, also known as eyelid tucks or lifts. With this skin removal, the overhang is removed and the natural crease or inward fold of the upper eyelid is seen again. While part of the underlying orbicularis muscle has historically been part of an upper blepharoplasty, contemporary techniques now seek to preserve it and to only remove skin.
Given the small area that eyelids occupy, it is not an uncommon request to ask if it can be performed under local anesthesia. While the use of local anesthesia for a blepharoplasty does not shorten one’s recovery from the swelling and potential bruising of the surgery, it does save anesthesia fees and the short-term issues related to having been put to sleep. The infiltration of local anesthesia can penetrate the thin tissues of the eyelid very effectively for a profound numbing and vasoconstrictive effect.
Blepharoplasty surgery can be very successfully done under local anesthesia. But it can not be so effectively used on the lower eyelid because of constant eyelid movement with the inability of the patient to not look at the ongoing surgery. Upper blepharoplasty is done with the patient’s eyelid closed and done from above or to the side of the patient, both maneuvers which prevent the patient from potentially seeing what the surgeon is doing. Thus lower eyelid surgery or combined upper and lower blepharoplasty surgery is best done under sedation or general anesthesia.
Case Highlights:
1) A blepharoplasty (eyelid lift) is very effective for eliminating hooding and skin overhang of the upper eyelid.
2) An isolated upper blepharoplasty can be comfortably done under local anesthesia for many patients.
3) Recovery from upper blepharoplasty can be very rapid and one looks reasonable in 7 to 10 days after surgery.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana


