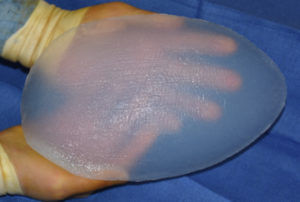
Hip augmentation is most commonly done using fat injections. Even for patients that do not have a lot of fat to harvest, enough can almost always be obtained to fill in indentations or divots on both sides of the hips. But when combined buttock and hip augmentations are needed or in a thin body type, fat harvest sites may be inadequate. In addition, not all fat injections to the hips are successful.
When fat injections is not option or has failed for hip augmentation, the only other option is the use of an implant. There is no standard or preformed hip implants. While some surgeons may try and use implants made for other parts of the body, the hip area requires a unique implant shape. This shape is more like that of a shaped buttock implant but with a lower profile at its peak projection.
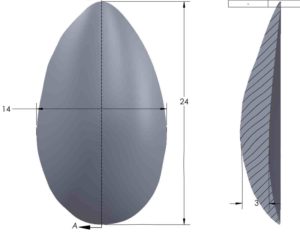
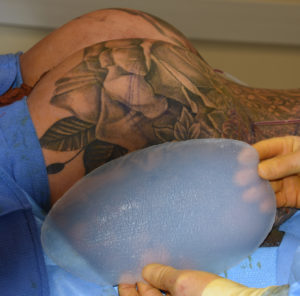
Custom hip implants provide a permanent augmentation to narrow or indented hips. They are an option when there is inadequate donor sites for fat injections or fat injections that have not persisted. When one has enough fat to do injections this should always be tried first as such injections improve the quality of the hip tissues even if its augmentation effect may turn out inadequate.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana