
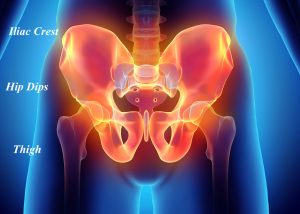
- Correct hip dips
- Create a more hourglass silhouette
- Complement previous BBL results when fat alone isn’t enough
- Done with rib removal waist reshaping surgery for a more feminine body contouring effect.
What makes hip implants unique?
Hip implants s are uniquely different from other aesthetic body implants due to their vertivcal orientation (onger than wide) on the sides of the hips, is a soft tissue non muscular augmentation, has a more superfiicial pocket location and exposes the implant to bending stresses with various leg movements.
Implant type
- Solid silicone elastomer (similar concept to buttock implants, but thinner longer and more contoured)
- There are no off-the shelf hip implants
Custom implants designs are needed. The optimal implant design is not yet known. But ‘smaller’ implant designs are more successful than larger ones. What has also been learned is that a medium durometer of stiffness is better than an ultrasoft material for both placement as well as preventing inferior edge bending diue to the vertically oriented shape of the implant.
Surgical placement
Can only be placed on top of the TFL fascia (deep subcutaneous plane), subfascial or submuscular are not options over the lateral pelvis/hip area
- Incisions are ;placed must below the iliac crest 5 to 7cms in length.
Need for prolonged drain use in the early recovery period.
- Can be combined with many other body contouring procedures:
- Liposuction
- Fat grafting
- Buttock augmentation
Rib removal waist/torso
Typical candidates
- Lean patients with minimal fat for BBL
- Persistent hip dips despite fat grafting
- Patients seeking predictable, permanent volume
- Those wanting lateral width rather than posterior projection
 Pros
Pros
- Immediate, stable volume
- Not dependent on fat survival
- Strong control over shape and symmetry
Cons & risks
- Higher complication rates than any other aesthetic body implant
- Seroma formation
- Implant edge visibility, occurs most commonly in lean patients (who often need them the most)
- Infection, implant removal
- Asymmetry
- Longer recovery than BBL-only approaches
Because of these risks, most surgeons avoid hip implants or have no to limited experience with them and prefer:
- Strategic fat grafting
- High-definition liposculpture
- Hybrid approaches (very small implant + fat camouflage)
Bottom line
Aesthetic hip implants can work, but they’re not first-line for most patients. They’re best for:
- Very lean bodies where fat isn’t available or has failed
- Revision cases
- Structural deficiencies fat can’t fix
Should be avoided in patients seeking large hip augmentation results as the complication risks get more significant the larger surface area coverage the implant has.
The optimal hip implant design is not yet known that works well in all patients. But the most effective designs that have the lowest risk of complications stay within the hip dip area. The more lean a patient is the more limited the implant surface area should be with lower projection profiles.
Custom hip implants are differetiated from the Pelvic Plasty procedure which is a skeletally based hip augmentation concept more commonly used in transfemales with congenitally narrow pelvic widths.
Dr. Barry Eppley
World Renowned Plastic Surgeon



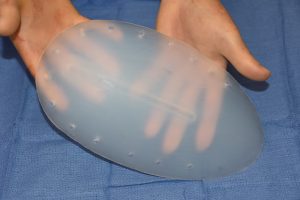
 Custom implants designs are needed. The optimal implant design is not yet known. But ‘smaller’ implant designs are more successful than larger ones. What has also been learned is that a medium durometer of stiffness is better than an ultrasoft material for both placement as well as preventing inferior edge bending diue to the vertically oriented shape of the implant.
Custom implants designs are needed. The optimal implant design is not yet known. But ‘smaller’ implant designs are more successful than larger ones. What has also been learned is that a medium durometer of stiffness is better than an ultrasoft material for both placement as well as preventing inferior edge bending diue to the vertically oriented shape of the implant. Can only be placed on top of the TFL fascia (deep subcutaneous plane), subfascial or submuscular are not options over the lateral pelvis/hip area
Can only be placed on top of the TFL fascia (deep subcutaneous plane), subfascial or submuscular are not options over the lateral pelvis/hip area
 Need for prolonged drain use in the early recovery period.
Need for prolonged drain use in the early recovery period.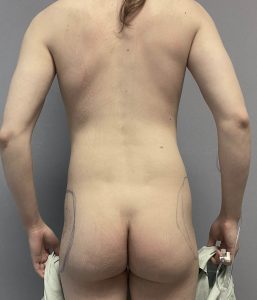
 Rib removal waist/torso
Rib removal waist/torso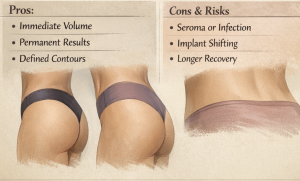 Pros
Pros