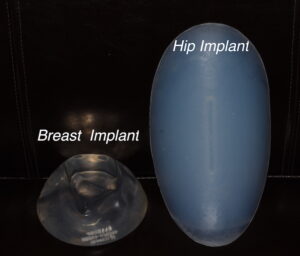
From an implant composition perspective breast implants are the only non-solid gel filled body implant. Every other silicone body implant is solid and not a two part implant design. (enveloping shell that contains a silicone gel material) Non-breast body implants have a soft lower durometer silicone material but they are nonetheless solid. Thus they are not prone to implant failure by shell disruption where the gel material can extrude out into the intracapsular space where a bodily response to the ‘free’ silicone can potentially occur.
Another very significant way in which breast implants differ from almost all other body implants is in the effect they are trying to create. Breast implants are designed to replace the feel of the soft tissue of the breast which is a fibrofatty tissue. Body implants are designed to augment a different type of soft tissue, that of muscle which is a somewhat denser type of tissue. As a result it is not necessary to have the ultrasoft feel that ‘a gel in a shell’ creates.
A not uncommon question about body implants is how much do they weigh and is their weight similar. This answer is best dressed by the principle of specific gravity which is a mathematical ratio of the density of a particular substance to water. The silicone gel of breast implants has a specific gravity less than 1.0, making the implant lighter than water. Thus silicone breast implants can be seen to float. Conversely a solid silicone implant (e.g., pectoral or calf implants) sinks in water due to a specific gravity that is greater than 1.0 making the material heavier than water.
Interestingly despite their physical differences in whether they float or sink, their actual differences in specific gravity is fairly small. Silicone gel is right under 1.0sg while solid silicone is just above it at around 1.2sg. But despite being only just above or below the density of water it affects how they respond when placed in it.
Despite what happens outside the body in a bathtub or swimming pool, the clinical relevance of their specific gravity differences is largely irrelevant since they are encased within a tissue pocket inside body that has an overall specific gravity of just under 1.0sg. (.974) Thus the body will still float whether it has one breast implants or other solid body implants. Solid silicone bony implants are about 20% less bouyant than breast implants but does not affect the body’s basic buoyancy in water.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana


