Gynecomastia is defined succinctly as male breast enlargement. While this description is accurate, it is overly simplistic. Gynecomastia is a wide spectrum of male breast problems caused by the growth of excess male breast tissue. This can range from the smaller areolar gynecomastias (puffy nipple), up to a size that resembles a large droopy female breast (giant gynecomastia), to a deflated sac of skin and sagging nipple. (elder gynecomastia) The quest for younger males is a completely flat chest with no nipple protrusion.
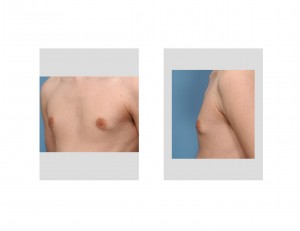
In presentation, this type of gynecomastia is not large and is fairly small. The actual firm mass underlying the areola is not large and it is fairly discrete, although bothersome to the patient. Many men may not be that bothered by it but young body-conscious males are very aware of it. This is particularly relevant in today’s male culture where a very flat chest contour is desired. Even a slightly puffy nipple stands out by these standards. For bodybuilders, this nipple mass is accentuated on flexing and in certain poses.
It is important to appreciate that although this areolar mass is small, it is not able to be removed adequately by liposuction. It is tempting to do so and I have tried because it seems like it should be easy to extract. I have not been successful even with laser liposuction. (Smartlipo) It can be reduced but not flattened sufficiently to the satisfaction of these male patients.
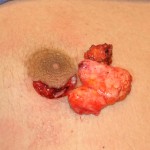
Dense areolar gynecomastia is best approached by doing open excision. Liposuction is tempting but will not be successful as the consistency of the mass is too dense.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana


