The scrotum is a dual-chambered containment tissue sac that contains the testicles and its neurovascular pedicles. It is composed of numerous tissue layers of which the most obvious is the overlying skin. This skin is unique in its appearance in which it has an irregular textured surface. Whilst often appears as thin skin, it is actually thicker than it looks probably due to the intimate attachment of the underlying muscle layer. (Dartos fascia)
They scrotal skin/sac is well known to be very stretchable and this is undoubtedly due to the combination of being a hanging structure, having contractile capabilities as part of its function and having no supportive backing. While the scrotum needs to be easily distensible, its size can become too big from various causes. Aging, large amounts of weight loss and pathologic conditions such as hydrocoeles (to name just one) can cause excessive scrotal skin to develop. When this occurs the enlarged scrotum can cause functional problems such as skin irritations and physically get in the way between the two inter thighs. There is also an aesthetic distraction to it if it hangs too low.
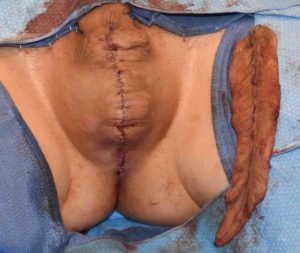
While scrotal skin is well known to scar well due to its hair-bearing composition, it scars best along the midline raphe. This is also the natural relaxed skin tension line of the scrotum. Its placement there also prevents the risk of scar contractors should incisions be placed on other part of the sac skin.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana


