Background: Hip implants are the newest implant method of augmentative body contouring. Their recent emergence as an aesthetic option for hip augmentation has been generated by the widespread popularity of fat injection buttock augmentation (Brazilian Butt Lift) and the need to have the lateral hip areas complement it as well as the lack of consistent success of fat injection hip augmentation. For thin women, just like in buttock augmentation, hip implants may be the only option due to lack of adequate body fat to harvest.
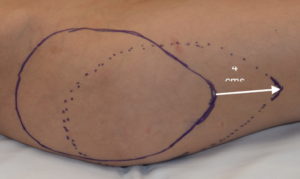
Hip implants poses several unique challenges compared to all other body implants. To get the correct position for most patients, the implant needs to be placed on top of the TFL fascia (suprafascial pocket) where the risks of postoperative seroma formation is significant. The incisional access to do so is often placed at the bikini line at a location where it can be hidden by clothes but is also at some distance from the inferior extent of the pocket. Also, due to the recent emergence of the use of hip implants no standard implant styles exist and it is not known what the ideal implant shape should be. (thus they are currently made custom for each patient)
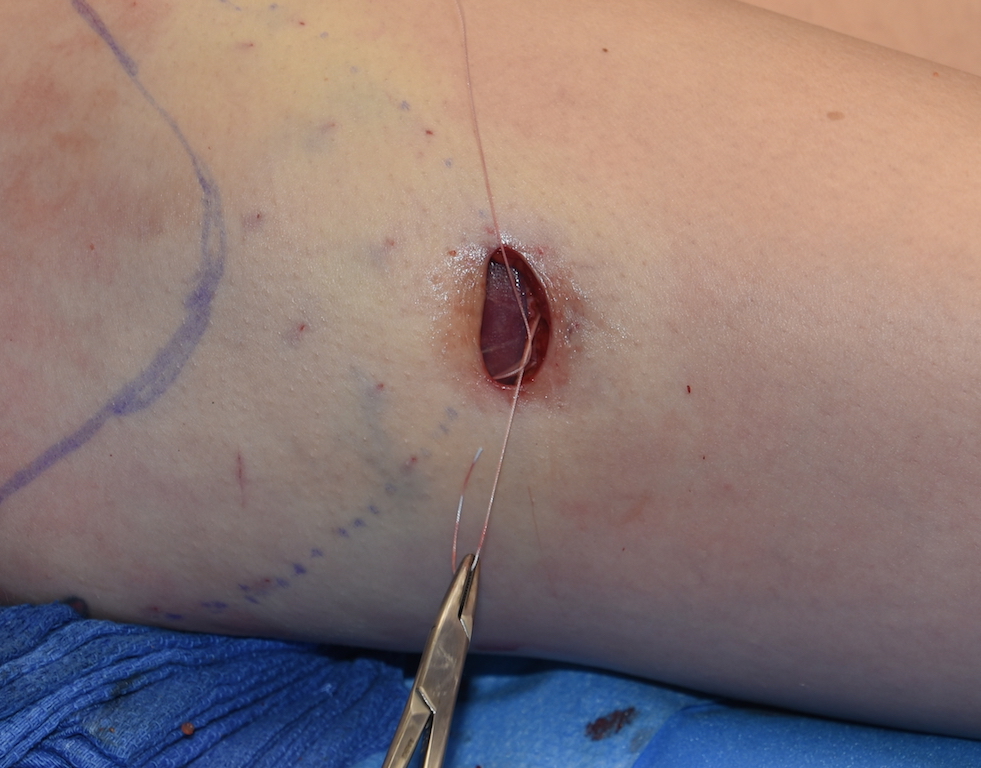
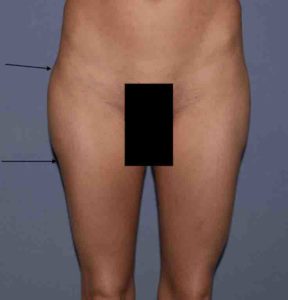
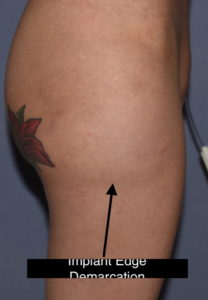
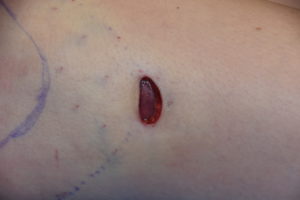
Due to the distance between the incision and the desired lowest end of the implant pocket, a highly positioned implant is one of the risks of the surgery. Should this occur the options for repositioning of the implant are challenging. How much it needs to be lowered will influence what type of implant repositioning approach is used.
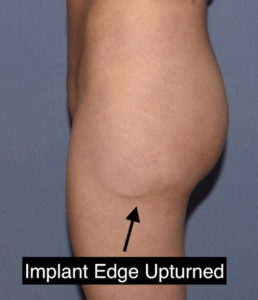
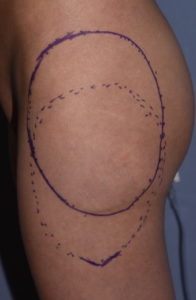
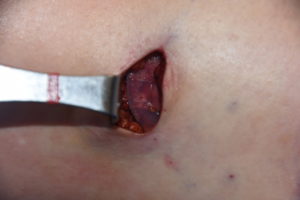
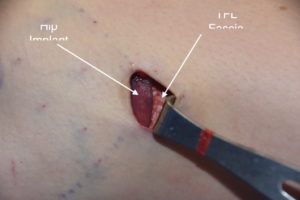
Postoperatively she was advised that the implant could slide back up as there remained the superior part of the pocket, lined with a capsule, which remained present. Circumferential compression wraps were applied to help keep the implant down in its new location as she healed. This is the one time that gravity works in the favor of the implant repositioning effort.
Case Highlights:
1) Inferior respositioning of high hip implants may be able to be done through the original incision or a new inferior incision is needed.
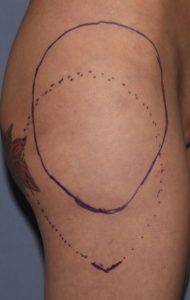
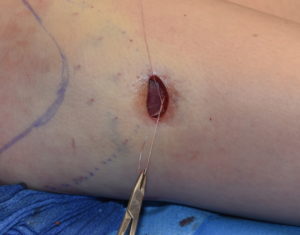
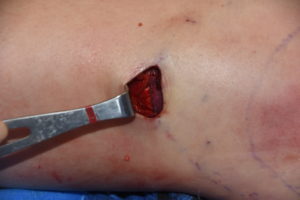
2) Due to the shape of hip implants capsulotomies need to be performed from the widest part of the implant and down along what lies below it.
3) A direct incision at the desired inferior point with suturing to the TF fascia is the most assured method of stable inferior repostioning in some patients.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana