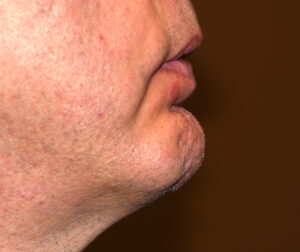
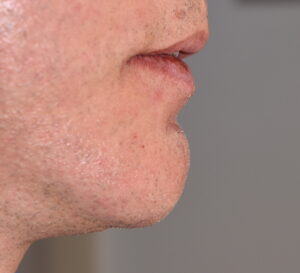
Background: The labiomental sulcus, often referred to as the labiomental fold, is the natural indentation at the upper extent of the soft tissue chin pad below the lower lip. Its depth varies based on genetics and bony chin shape. It represents the bony origin of the mentalis muscle attachment and the depth of the intraoral vestibule. The aesthetics of the sulcus depth can be debated but its general morphology should be that of a subtle curved concavity.
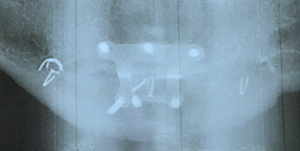
The depth and shape of the labiomental sulcus can be affected by various types of aesthetic chin surgery. Chin augmentation, whether done by an implant or a siding genioplasty, will almost always make the sulcus deeper. How much deeper depends on the amount of chin augmentation and the natural depth of the presurgical sulcus.
A chin implant makes the labiomental sulcus deeper by pushing out the soft tissue chin pad beneath it. A sliding genioplasty makes it deeper by pushing the bone out beneath it…and also creating a bony shelf or step off in the shape of the bone beneath it. That is a unique bony shape alteration that can lend itself to a significant deepening effect from scar contracture.
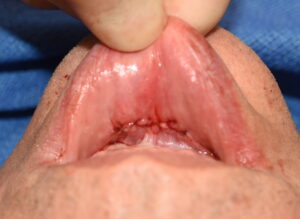
There is a big difference between a labiomental sulcus that naturally gets a bit deeper because of movement of the soft tissue pad beneath it vs the labiomental sulcus that gets pulled into the bony step off of a sliding genioplasty. The latter represents a true scar contracture deformity and requires a traditonal approach to any type of scar contracture deformity….release and the placement of something to prevent its recurrence. While fat injections may work for the subtle and rolling concavity of a deeper labiomental sulcus, that approach will rarely work for a fixed scar contracture. This determination can be made non-surgically through injections of saline or filler materials. If the labiomental sulcus comes out with any type of injection then fat injections will be successful. If not then a formal release and en bloc soft tissue graft is needed.
Case Highlights:
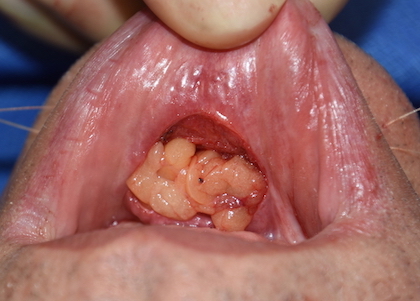
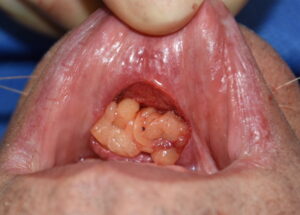
1) Labiomental sulcus contracture after a sliding genioplasty causes a v-shaped deformity, tight lower lip and a vertical shortening of the chin height.
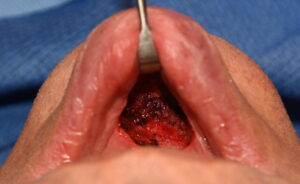
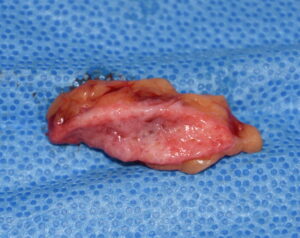
2) Labiomental sulcus contracture is treated by release and an interpositional soft tissue graft if it fails the injection test.
3) A autologous dermal fat graft is a good interpositional material to provide a sustained labiomental sulcus release and unfurling of the soft tissue chin pad.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana