Background: The reconstructive need for an implant to replace a loss testicle due to pathologic and traumatic reasons has been around almost as long as the removal procedures have been done. Historically silicon testicle implants had been used but they were formally removed from the US market in 1991 due to the breast implant fiasco. An FDA approved testicle implant did not emerge for years after that and when it did it was a saline filled implant, paralleling the use of saline filled implants in breast surgery.
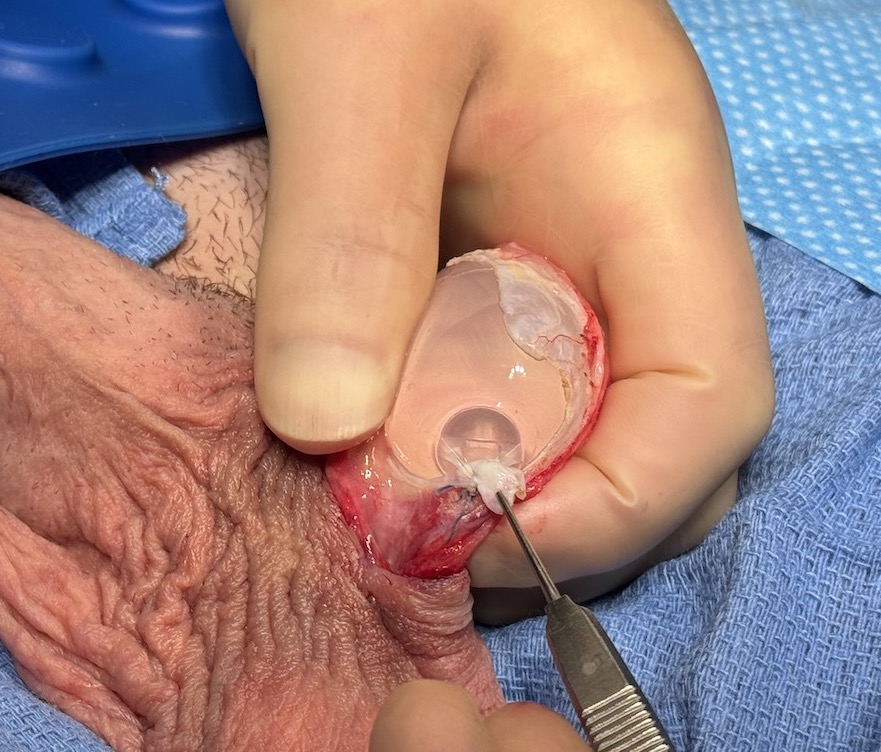
While saline testicle implants played a useful role when no other alternative implant style existed their use today is plagued by the natural limitations of the concept. They have a very hard unnatural feel as it is essentially water placed into a thick implant shell. This unnatural feel combined with the surgical technique of suturing the implant into place with a permanent suture creates an immobile high position of the implant. In some cases the feel and pull of the suture from any implant traction can create discomfort as well.
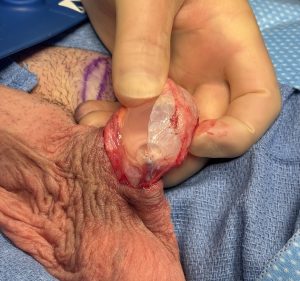
The principles of treatment of an undersized malpositioned hard testicle implant would be the same same as any other body implant. Specifically implant removal, total capsulectomy, inferior pocket expansion and replacement with a larger softer implant style.

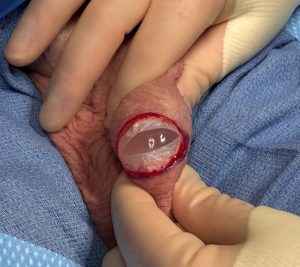
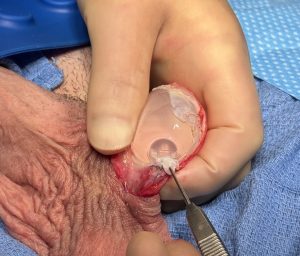
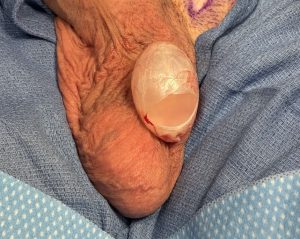
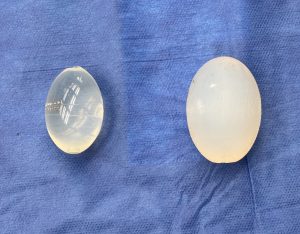
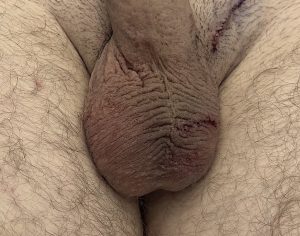
While the saline testicle implant had its historic role when no other implant option was available contemporary silicone testicle implants offer improvements in both feel and size. In addition the use of suture fixation of an implant in his pocket is outdated and unnecessary and causes numerous aesthetic problems with no obvious benefit. The implant replacement does not need to be attached and should be allowed to have good mobility in an implant pocket that is adequately low in the scrotum.
Key Points
1) The hard high testicle is synonymous with the use of a saline-filled implant replacement.
2) Implant removal, capsulectomy with suture removal and implant replacement is the solution.
3) Solid ultrasoft silicone testicle implants with a better size match to the opposite natural testicle is the superior replacement.
Dr. Barry Eppley
World-Renowned Plastic Surgeon