Background: There are numerous dimensional considerations in forehead surgery. The contour of the forehead is controlled by the shape of the underlying bone centrally and the temporal muscles laterally which can be modified by either augmentation or reduction. The vertical length of the forehead, however, is controlled by the soft tissue landmarks of the frontal hairline superiorly and eyebrows inferiorly. As a result changing the vertical length of the forehead requires soft tissue shortening or lengthening.
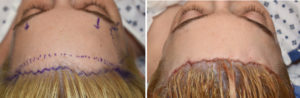
The most common soft tissue problem of the forehead is excessive vertical length. A length of 6.5cms or more of length between the eyebrows and the hairline is considered excessive. Most women who feel their forehead is too long are at that number or more. A frontal hairline advancement is the definitive treatment for shortening the vertical length of the forehead. The success of this procedure is highly dependent on the natural elasticity of the scalp. Shortening of the forehead is often associated with adjustment of the eyebrow levels as well. The combination of a frontal hairline advancement with a browlift works synergistically for vertical forehead shortening.
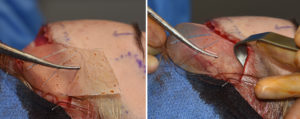
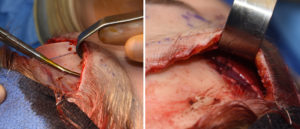
Many vertically long foreheads in females are associated with a narrow forehead or temporal hollowing. Widening of this forehead dimension also works well with vertical forehead reduction and can be accomplished by the insertion of subfascial temporal implants through the frontal hairline incision.
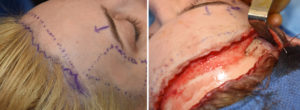
Case Study: This female desired to have a shorter forehead and augmentation of her temporal hollowing. She also desired a slight browlift effect as well.

Case Highlights:
1) Vertical forehead reduction reduces the distance between the hairline and the eyebrows through scalp mobilization and frontal hairline advancement.
2) Through the frontal hairline incision anterior temporal implants can be placed for concurrent temporal widening.
3) The frontal hairline advancement can be combined with a browlift to enhance the vertical forehead reduction.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana