Background: Hip augmentation is a feminizing body procedure for which there is no yet firmly established techniques to do so. Synthetic fillers are a non-surgical method but the high volume of injectate needed and the lack of permanent fillers with a high safety profile limit their use and effectiveness. While fat injections are a widely used surgical method it consistently fails to produce good results due to a high rate of resorption. This leaves implants as the one consistent method of hip augmentation that provides assured augmentation and is surgically safe.
Hip implants, however, are not free of complications primarily due to implant location and the unique features of a lot of bending and rotational motion across the implant site. Hip augmentation also is a variable concept in terms of the zone or location of the augmentation needed. Different implant techniques are needed for the various hip augmentation zones and the patient’s specific hip augmentation goals. In essence hip augmentation differs from most other aesthetic body augmentations as it is not a single augmentation concept that applies to everyone seeking an enhancement procedure.
One type of hip augmentation is bony-based for the patient whose hip deficiency is strongly influenced by a narrow pelvic width. This is a common concern in transfemales with a congenital high angled ilium or the cis-female who has very narrow hips. It could also be for the patient, regardless of gender, in which their lower hips/thighs have disproportionate width compared to that at the iliac crest level. Hip augmentations in these patients is known as Pelvic Plasty, a hip augmentation method that focuses on widening the bony iliac crest and the subiliac fossa below it.
The immediate before and result during surgery showed the improvement in bony hip width and the augmentation of the subiliac fossa/indentation below it.
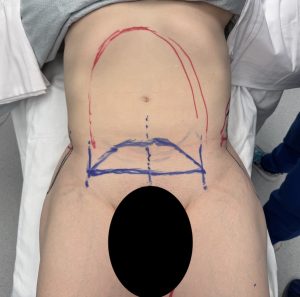
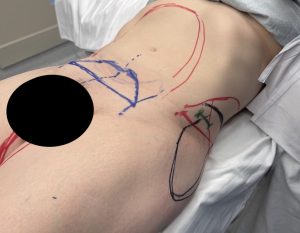
Case Study: This female desired an increase to her iliac crest width. She had adequate lower hip width/fullness but at the upper hip area question was much more narrow with a significant indentation/crease across the area below the iliac crest into the upper thigh/inguinal area. She was also scheduled to undergo abdominal, flank and inner thigh liposuction with a mini tummy tuck.
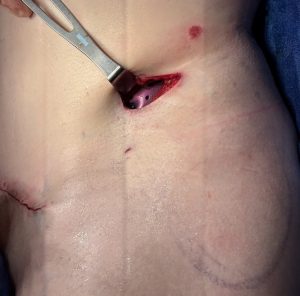
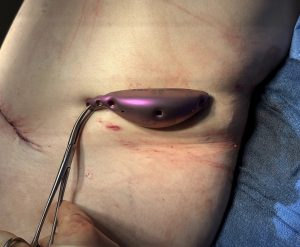
Once the iliac plate was in position a specially designed hip implant to fill the subiliac fossa was placed on top of the gluteus medius fascia below the plate and attached to it by its design.
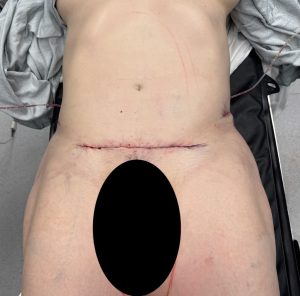
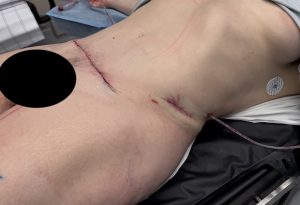
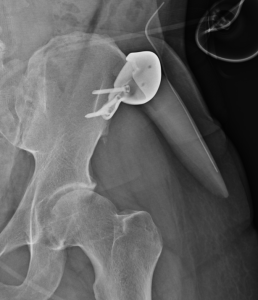
Key Points
1) The composite titanium mimic crest plate with silicone hip implant is for hip augmentation in the narrow pelvic width patient.
2) The metal plate attaches to the anterior iliac crest while the silicone implant fits into its underside for a more complete upper hip augmentation effect.
3) Skeletal-based hip augmentation is often a combined bony and soft tissue implant concept.
Dr. Barry Eppley
World-Renowned Plastic Surgeon