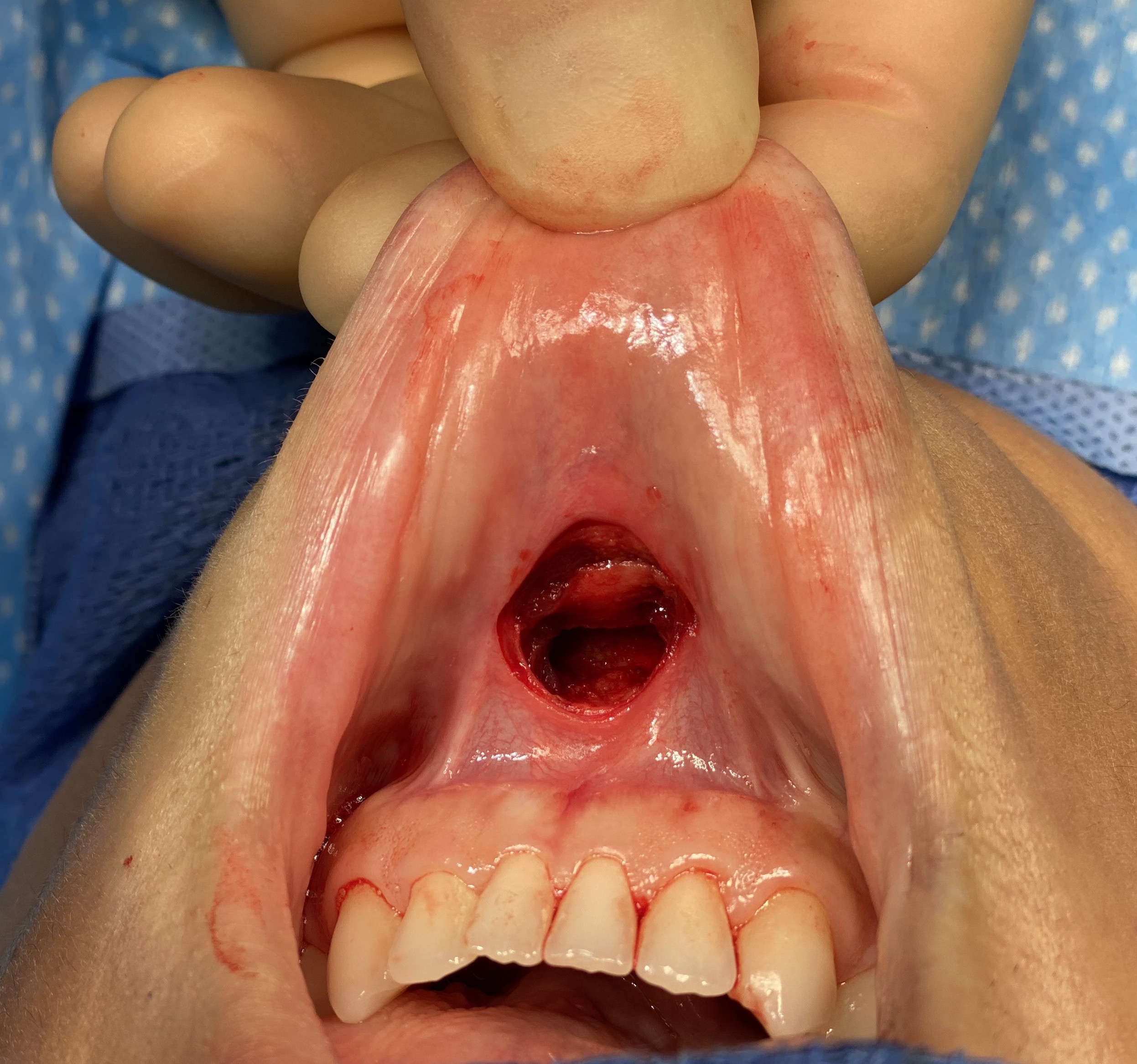
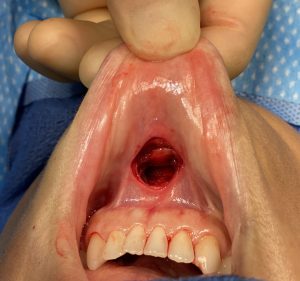
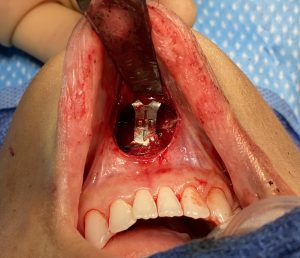
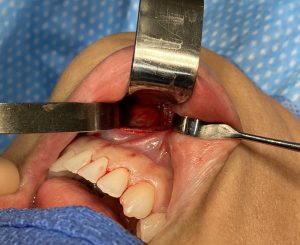
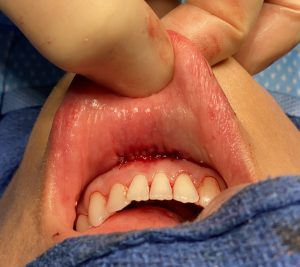
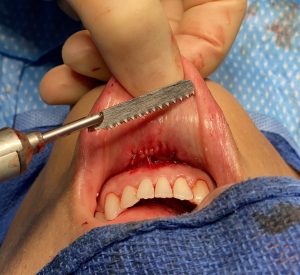
The well known sliding genioplasty is sometimes selected by patients because they wish to avoid a submental scar from a chin implant. The incision location may not be the primary reason but may on the list of several motivations for choosing a bony chin augmentation procedure.While an intraoral incision avoids a scar it has its own potential disadvantages, which while hidden from view, does not mean they are irrelevant.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana