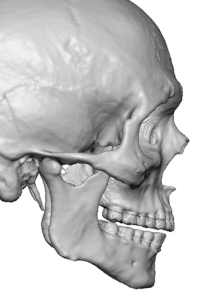
Custom jawline implants can play a meaningful role in improving the appearance of the aging neck in older men, but their effect is structural — not a replacement but as an enhancement for soft-tissue rejuvenation. The improvement comes from restoring bony projection and tension to the lower face–neck junction.
Here is how they have their structural influence:
1?? Restoring Skeletal Support at the Cervicomental Angle
With aging, men often develop:
- Loss of jawline definition
- Blunting of the cervicomental angle (neck–chin angle)
- Jowling that spills over the mandibular border
A custom jawline implant — due to its wraparound design — increases:
- Chin projection
- Mandibular border width
- Jaw angle definition
This stronger skeletal framework:
- Pushes the soft tissue envelope outward and upward
- Improves the visual separation between face and neck
- Sharpens the cervicomental angle
The neck is lifted by the pull of the jawline implant above it.
2?? Creating a Stronger “Ceiling” for the Neck
Think of the jawline as the structural ceiling of the neck.
In older men:
- Soft tissue descends
- Platysma laxity increases
- Submental fullness becomes more noticeable
By enlarging and defining the mandibular border:
- The overhanging appearance of jowls is reduced
- Submental fullness looks proportionally smaller
- The neck appears less heavy from profile view
This is also a proportional improvement as well as a true lifting/tightening effect.
3?? Improving Neck Profile Without Touching the Neck
In patients with:
- Mild to moderate neck laxity
- Adequate skin tone
- No severe platysmal banding
A custom implant can significantly enhance profile aesthetics without a neck lift.
Projection changes alter the visual balance between:
- Chin
- Neck
- Lower lip
A recessed chin exaggerates neck fullness. Advancing the chin reduces that imbalance.
4?? Enhancing Masculinity in the Aging Lower Face
Older male necks often look aged because:
- The jawline narrows
- The chin becomes less projected relative to soft tissue bulk
A wider, stronger mandibular border:
- Counteracts soft tissue descent
- Restores masculine geometry
- Improves side and three-quarter views
Sharpening the neck-face transition by outward expansion has a masculinizing effect in men.
5?? When It Works Best
Custom jawline implants improve the aging neck most when:
- The primary issue is skeletal deficiency
- There is moderate soft tissue laxity
- The patient wants structural enhancement
They are less effective alone when:
- There is significant skin redundancy
- Prominent platysmal banding exists
- There is heavy submental fat
In those cases, combination procedures are common:
- Jawline implant + submental liposuction
- Jawline implant + neck lift
- Jawline implant + lower facelift
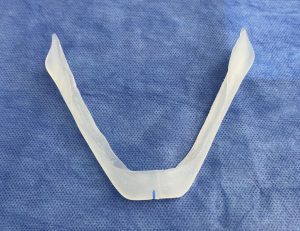
6?? Why Custom Design Matters in Older Men
Older men often have:
- Thicker soft tissue envelopes
- More variable asymmetry
- Heavier jowling
A custom implant allows:
- Increased vertical height along the mandibular border
- Strategic jaw angle widening
- Chin projection matched to neck contour
Standard implants usually do not address these nuances.
Important Clarification
Jawline implants do not:
- Tighten skin
- Remove fat
- Correct muscle laxity
They improve neck aesthetics by strengthening the structural framework underneath.
Summary
Custom jawline implants improve the aging neck in older men by:
- Restoring mandibular definition
- Enhancing chin projection
- Improving cervicomental angle appearance
- Providing structural support to sagging tissues
- Increasing masculine lower face geometry
They are a skeletal solution that visually upgrades the neck–jaw relationship.
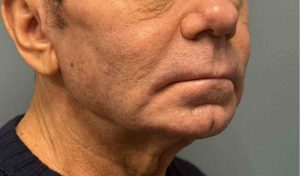
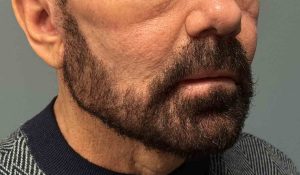
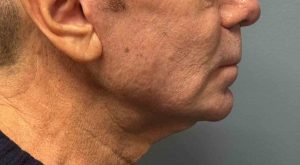
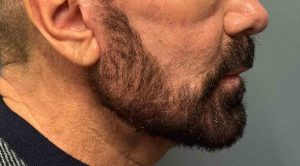
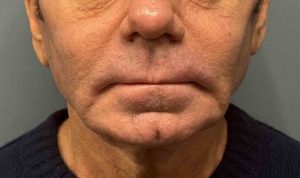
Case Study
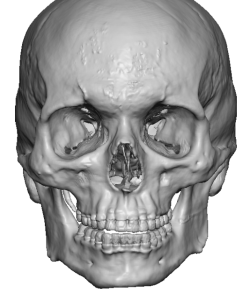
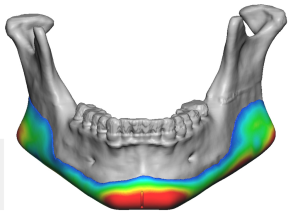
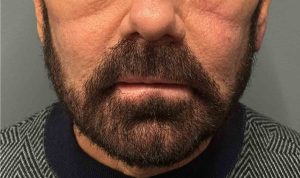
Discussion
Older male patients are not simply “aged younger men.”
They present with distinct structural and soft-tissue characteristics that directly influences implant design.
Older male jawline implant designs often differs from younger male design.In older men:
- The mandible itself typically does not shrink significantly unless there is major tooth loss.
- However, the jawline appears weaker because soft tissue bulk increases and descends.
Planning Implication:
Avoid undercorrecting implant projections. Skeletal support must be strong enough to overcome loose stretched soft tissues.
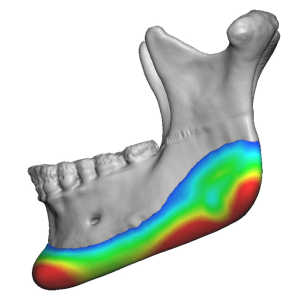
Increased Vertical Mandibular Border Height
Adding vertical height along the inferior mandibular border:
- Helps sharpen cervicomental angle
- Creates stronger jaw–neck separation
- Counters jowling visually
Stronger Chin Projection
Advancement of 6–10mm is often needed to:
- Rebalance submental fullness
- Improve neck projection relationship
- Strengthen profile dominance
Older men frequently require more projection than younger patients because of thicker soft tissues.
Controlled Jaw Angle Widening
Moderate widening:
- Restores masculine width lost with aging
- Provides posterior support to descending tissues
- Improves 3/4 view significantly
Avoid excessive lateral flare, which can look unnatural in mature faces.
Overcorrection vs Undercorrection
Younger patients:
- Risk of overprojection
Older male patients:
- Risk of underprojection (most common mistake)
Because:
- Thick soft tissues mask subtle augmentation
- Small changes are often visually insignificant
Custom design allows more precise volumetric correction than stock implants.
Combination Procedure Planning
Common combinations in older men:
- Custom jawline implant + submental liposuction
- Custom jawline implant + anterior platysmaplasty
- Custom jawline implant + limited neck lift
- Custom jawline implant + lower facelift
Sequence matters:
- Structural implant first
- Then adjust soft tissue to new framework
Surgical Decision Tree:
|
Soft Tissue Status |
Implant Alone |
Combine Procedure |
|
Mild laxity |
Often sufficient |
Optional liposuction |
|
Moderate laxity |
Helps profile |
Consider submental lipo |
|
Severe laxity |
Insufficient alone |
Add neck lift/lower facelift |
Long-Term Aging Considerations
The implant:
- Remains stable
- Does not age
- Does not cause resorption of the jawbone
Soft tissues:
- While they will continue to age they age better due to the added structural support beneath them (age resistance)
- Will lessen the magnitude or need for secondary soft tissue procedures.
Summary
In older male anatomy, custom jawline implant planning requires:
- Stronger skeletal augmentation than younger men
- Strategic vertical height addition is some cases
- Controlled width enhancement
- Often combined with certain neck procedures or more aggressive soft tissue management done secondarily.
The key principle:
Improve the structure first. Then refine the soft tissues.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Plastic Surgeon