
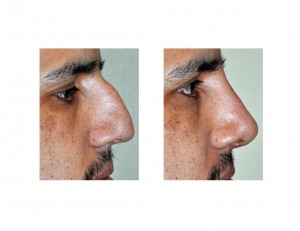
Admittedly I do not follow New York mets baseball and had never seen Jonathon Niese before. But in first seeing his pictures before the rhinoplasty, he did have an impressive nasal deformity marked by an extremely large dorsal hump and downturned tip. Such large Roman-style noses are caused by a strong underlying growth of the septum which pushes the bridge of the nose upward, most impressively at the junction of the nasal bones and upper lateral cartilages. The septum may frequently be deviated or bowed and can interfere with rapid breathing during exercise. Whether correction will make him an improved pitcher remains to be seen, but it will most certainly allow him to have better conditioning with improved nasal air exchange.
The Roman or aquiline nose is a classic nasal shape that has been known for thousands of years. It is also called the hook or beak nose because it appears with a prominent bridge in which the tip is bent downward. It occurs in numerous ethnic groups and historically and in some countries today it is a sign of character or masculine strength. In most of the world today, particularly in Western cultures, the Roman nose violates contemporary standards of facial aesthetics. A smooth dorsal line (bridge) and a tip that is closer to at least a 90 degree nasolabial angle with the lip is viewed as more attractive and in better facial balance.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana


