Background: The ear is remarkably resistant to the effects of aging and gravity due to its largely cartilaginous framework composition. The ear generally does not sag or drop with aging with the exception of the earlobe…the only non-cartilaginous part of the ear. The earlobe is well known to become longer due to the stretch of its thin soft tissues which is enhanced by the use of ear rings and in the unattached or inverted V shape earlobe attachment to the face. (where the inferior helical rim has a U shape and generally a larger earlobe)
Besides the earlobe the rest of the ear does not usually change shape due to its strong cartilage insertion into the bony ear canal pinning it to the side of the head. Thus no vertical lowering of the ear occurs over time. There may be some slight outward protrusion over time but often this is just a perception as the hair above and around the ear often becomes less with age particularly in men. Some protrusion of the ear may have always existed but was less visible with more or longer hair.
Rejuvenation of the ear is about improving its shape and shortening its vertical length. A better shape often refers to a less obtuse or more acute auriculocephalic angle. How close the ear sits to the side of the head is not really an age issue but the more the ear sticks out the less appealing it is to some people. The longer earlobe is the real aging ear issue but also the simplest one to improve.
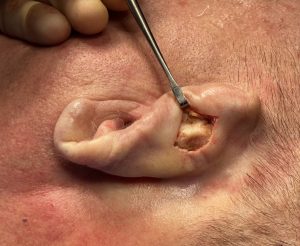
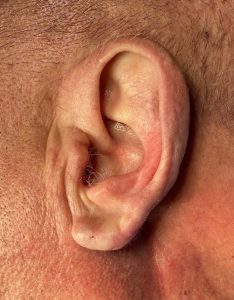
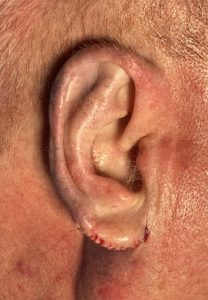
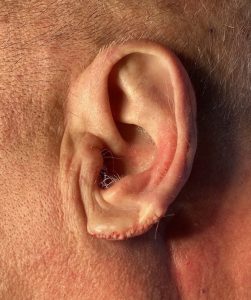
Case Study: This older male was bothered by a modest protrusion of the upper third of his ears and elongated earlobes. He had a visible antihelical fold which is a testament to that the upper protrusion was not excessive which occurs when no antithelical fold is seen at all.
Case Highlights:
1) In the older male or female the shape of the ear is affected by the aging process, most notably lengthening of the earlobe.
2) Minor amounts of ear protrusion when young may not be a concern but with age and lengthening of the earlobe it may be more of an aesthetic issue.
3) Rejuvenation of the older ear can be done by a few minor adjustments such a little cartilage setback and some earlobe reduction.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana