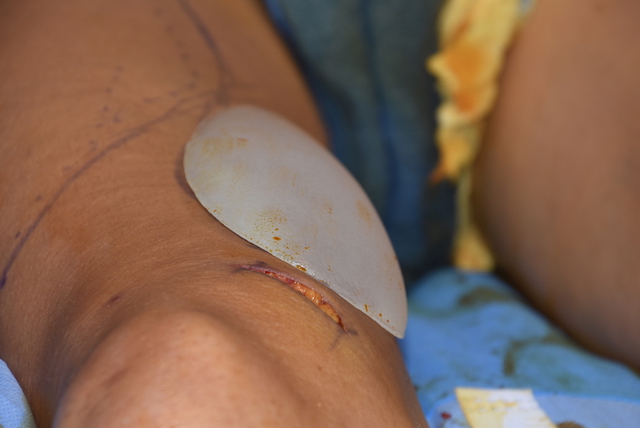
The most common leg muscle that is augmented for aesthetic purposes are the calfs. (gastrocs) Calf implants have been used for decades and are a very successful body implant procedure. In more recent times the upper leg has been periodically implanted as well to augment either the rectus femoris or the combined rectus femoris-vastus laterals muscle combination of the anterior thigh.
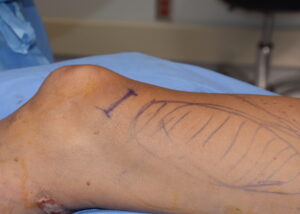
One very rarely augmented thigh muscle is the vastus medialis. This muscle is part of the quadriceps which consists of the vastus medialis, intermedius and lateralis and the more midline rectus femoris muscle. The most commonly augmented thigh muscle is the rectus femoris as it runs straight down the front of the thigh. The vests medialis is the most medial or inner of the quad muscles. When it is enlarged, as is seen in body builders, it creates a defined bulge at the inner and superior aspect of the knee.
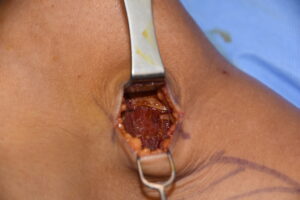
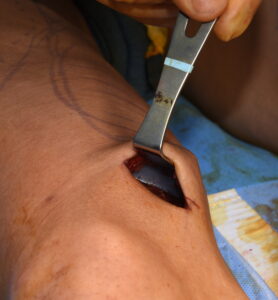
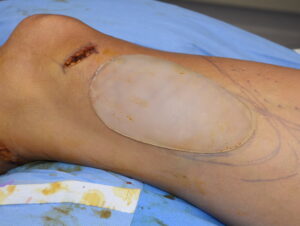
Numerous lower leg muscles can be augmented with implants including the gastrocnemius, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis as well as the vastus medialis. The key is to place a relatively small incision that provides indirect to close access to create the subfasial pocket. As a general rule you want the incision and final scar to not be directly overlying the implant. This prevents scar edge inversion as well as the risk of muscle contraction abnormalities due to adhesions.
The suprapatellar skin incision
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana