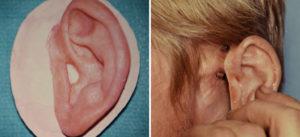
Background: Loss of an ear can occur from a variety of reasons including cancer resection and traumatic avulsion. Such ear amputations pose major reconstructive challenges which can be done using an autogenous method (cartilage framework and vascularized soft tissue cover), completely prosthetic method (ear prosthesis) or a combination of both autogenous tissue and prosthesis. (synthetic ear framework with vascularized soft tissue cover)
While I typically prefer some form of autogenous reconstruction, there is a role for a completely prosthetic ear reconstruction approach. There is no denying that a prosthetic ear created by a Maxillofacial Prosthetist creates the best match to the opposite ear. But the long-term success of an ear prosthesis is directly related to the patient’s comfort in wearing it. If the patient has little confidence that it will stay in place then they are unlikely to use it.
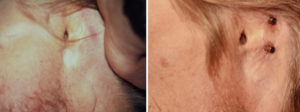
While prosthetic ears were once held in place by adhesives, this is not a reliable method for stabilizing something to the side of the head..Borrowing from dental implant technology, the use of osseointegrated implants has long eclipsed the use of adhesives by providing a bone anchorage method for prosthetic stability.
Case Study: This 35 year-old male had his left ear removed due to melanoma skin cancer. He also had a superficial parotidectomy and sentinel lymph node biopsy. This left him with Frey’s syndrome as well as the absence of his ear. He opted for a completely prosthetic ear reconstruction method.
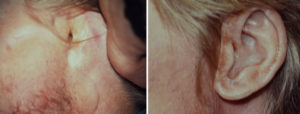
While a prosthetic ear creates the best looking ear, it will require maintenance on a regular basis. The implant posts must be kept clean so a tight soft tissue collar is maintained. (much like the gums tissues around a tooth) The ear prothesis will need periodic replacements due to color fading and the wear and tear from daily use.
Highlights:
- The stability of prosthetic ear reconstruction depends on osseointegrated titanium implants.
- Osseointegrated implants need a tight soft tissue collar for long-term retention.
- The patient will require multiple prosthetic ears over time due to material aging and discoloration.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana