The use of breast and buttock implants are well established for aesthetic body augmentations and have a high degree of clinical success. Their success rate is largely dependent on the depth of the tissue pocket in which the implant is placed and the shape of the implant. An under the muscle (thick well vascularized tissue cover) location and a round or hemi-spherical implant shape (looks the same no matter how it is positioned) provides both an effective augmentation result and good long-term tissue tolerance . This explains why they are both frequently performed and have an acceptable rate of complications.
While hip implant augmentation is a frequently requested procedure it is very different than breast or buttock implants. Besides the more superficial and less thick soft tissue pocket location hip implants are not round. The hip area is not a spherical mound like the breasts or buttocks. This makes the implant design needed to augment it is different.
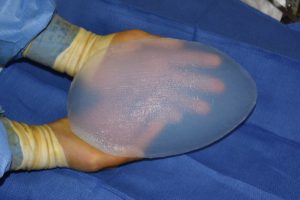
This paper defines the process of planning, designing, and fabricating a custom hip implant with significant patient input. By definition, patient-specific or custom implants can be any shape, size, and projection. The patient and surgeon provide the implant fabrication company a paper tracing of the surface area of the proposed implant along with the maximum projection. Engineering creates a 2-dimensional drawing using a computational software for intelligent system design or CAD. The implants are fabricated with input from the surgeon on silicone material softness (durometer), implant alterations to lower weight and enhance ease of folding for placement, and shape.
Dr. Barry Eppley
World-Renowned Plastic Surgeon


