Background: Many of aesthetic surgery procedures borrow from established reconstructive surgery techniques and then are modified and applied in a more aesthetic manner. Much of this re-application comes down to performing the procedure with less scar burden through smaller incisions. Such small or hidden incisions are especially important in all forms of aesthetic facial surgery.
The need for limited incision access is just as important in all forms of facial implant surgery. One fundamental difference between standard and custom facial implants is size, most custom facial implants cover large surface areas of bone. They may not necessarily be thicker but they are definitely longer in length most of the time. Getting such custom implant into position in the face poses greater challenges than standard implants but the need for limited incisions remain.
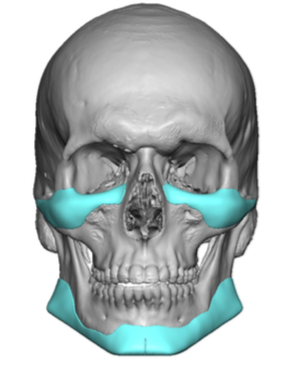
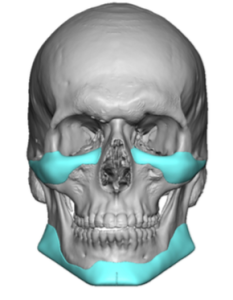
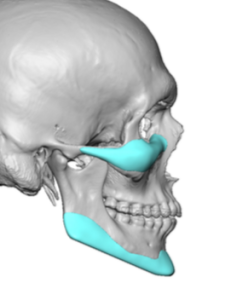
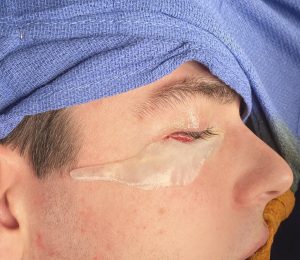
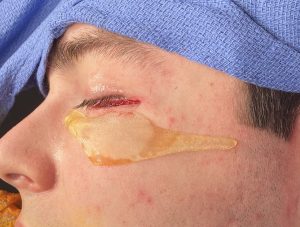
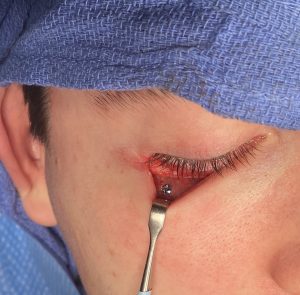
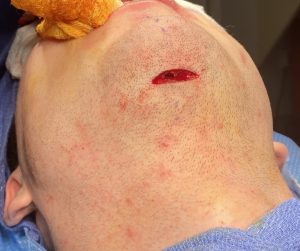
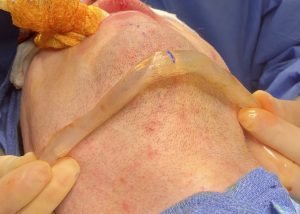
The now classic male facial masculinization procedure is the combination of custom infraorbital-malar (IOM) and jawline (JL) implants. Both create long horizontal lines of facial bone augmentation of existing bone structures that have varying degrees of 3D deficiencies. The custom IOM implant extends from the medial infraorbital rim all the way back along the zygomatic arch creating varying degrees of the high cheekbone look and improving undereye hollows. The lower eyelid incisional approach provides the best access as it allows for a straight line of dissection and implant placement. The JL implant provides a definitive linear line of separation between the face and neck while creating more prominent JL corners of the chin and jaw angles. It requires three incisions to do the anterior chin which provides a line of dissection that parallels the implant and paired intraoral incisions which allows for a perpendicular line of dissension. (whose relevance will be discussed below)
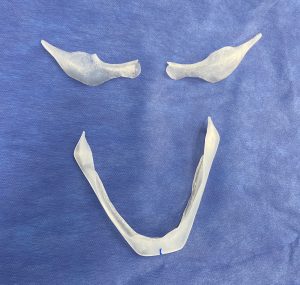
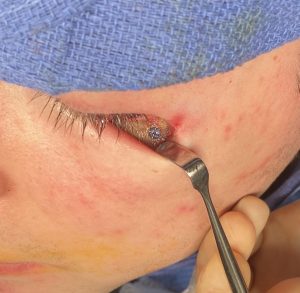
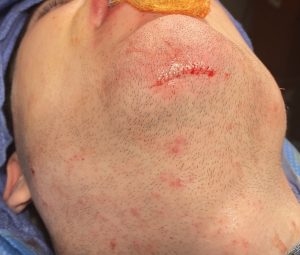
One of the important concepts in custom IOM and JL implants is their long lengths require an extended subperiosteal pocket dissection. The most effective and assured method of creating the tissue pocket needed over the exact area of the bone needed for implant placement is to parallel that of the implant’s design. This is why the eyelid incision for IOM implants and the submental skin incision for jawline implants is the best incisional choices. Trying to place an IOM implant from an intraoral approach or a jawline implant from an anterior vestibular intraoral approach has a much higher risk of implant malposition. This also explains why that the jaw angle portion of the jawline implant, or even standard jaw angle implants, has a significant risk of malposition. Coming from a perpendicular point of access from the length of the implant, although there is no choice in placing implants in this facial area, does not allow the best line of access for the implant’s location on the bone.
Case Highlights:
1) Custom facial implants are often longer in bone surface coverage which poses challenges for surgical placement.
2) The male facial masculinization procedure consists of two fundamental lines of facial augmentation, the infraorbital-malar and jawline.
3) While it takes five (5) incisions to place custom IOM and jawline implants none have lengths greater than 2.5cms and two of them are completely intraoral.
Dr. Barry Eppley
World Renowned Plastic Surgeon