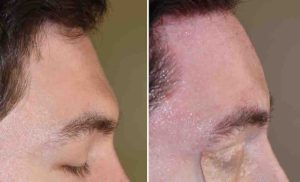
Background: Brow bone reduction today is most commonly associated with facial feminization surgery. But the reality is that cis-males can also be bothered by excessive brow bone protrusion. The difference between a cis-male and a transgender male to female brow bone concerns are one of magnitude. While the transgender patient wants to take a normal male brow bone and reduce it the cis-male has an abnormally large brow bone and wants to reduce it to a normal size one.
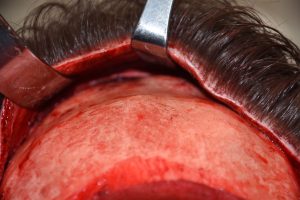
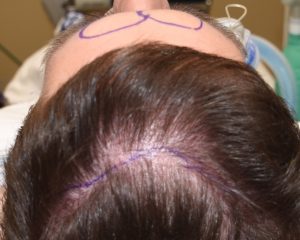
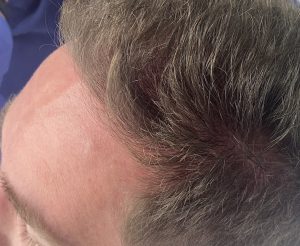
It is not that the male brow bone reduction surgery is any harder or easier than that of facial feminization patients it is usually just a larger starting point. What is different, however, is the incisional consideration. The cis-male may have a good frontal hairline and hair density but many do not. The one universal incision concept amongst men is that a transcoronal incision (ear to ear) is not going to be accepted., Where to put the incision is the key question and its location can determine whether the patient may or may do the surgery.
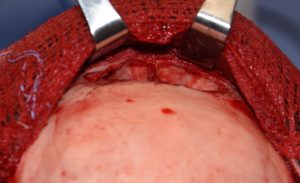
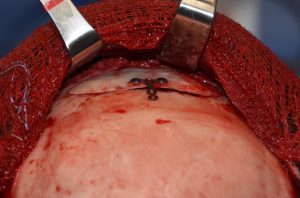

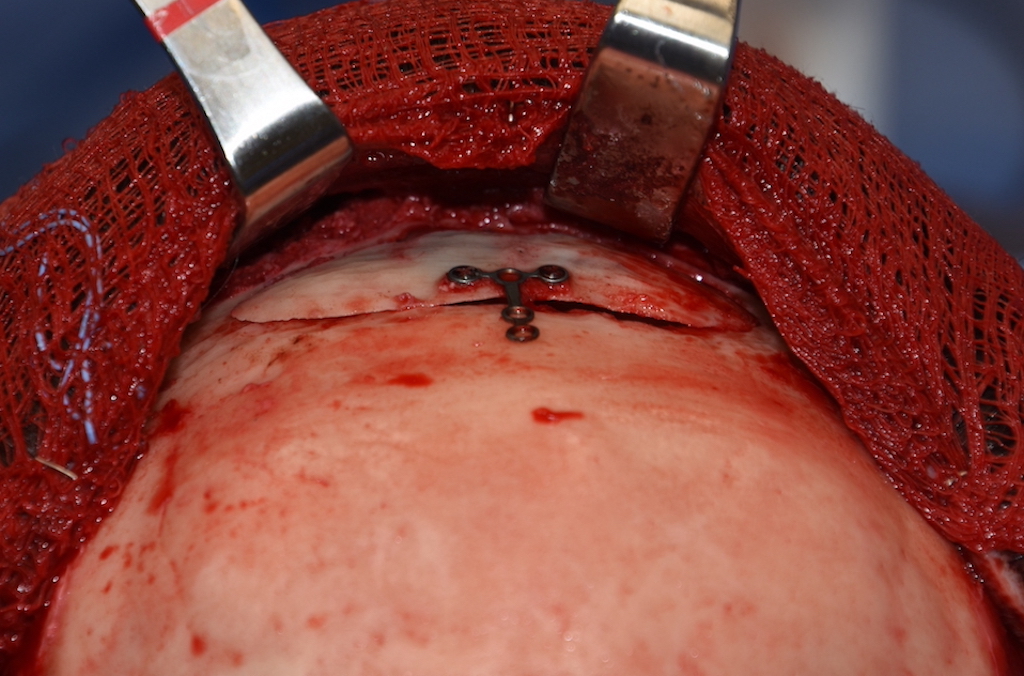
One of the most intriguing aspects of bone flap setback brow bone reduction surgery is why it works. You cut off a thin piece of bone over the frontal sinus and modify it by burring. It is now a devascularized piece of bone that is put back over an open frontal sinus…with the vast majority of the thin bone having no bone contact or blood supply. Yet somehow the bone survives and goes on to heal without being completely absorbed.
Key Points:
1) Male brow bone reduction has the challenge of incisional placement.
2) Almost all male brow bone reductions need a bone flap removal technique.
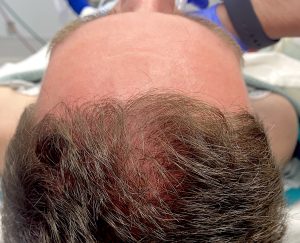
3) Long term results shows a healed reduced brow bone and a well healed scalp incision.
Dr. Barry Eppley
World-Renowned Plastic Surgeon