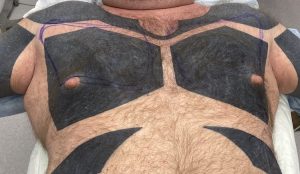
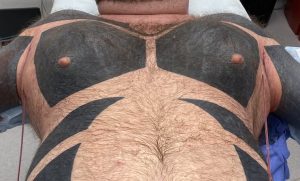
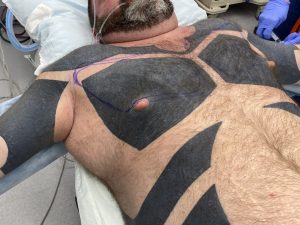
Background: Pectoral implants are the male equivalent of the female breast implant….sort of. While breast implants may be placed partially submuscular their objective is to create a larger and rounder soft tissue breast mound. Conversely pectoral implants are placed submusucular with the specific intent of creating a larger muscle appearance and not a round mound appearance The overlying soft tissue only expands within the framework of the underlying muscle. This speaks to the need to not violate the inferior pectoralis major muscle attachments during their placement.
While breast implants have a fairly standardized approach to choosing their size (base diameter and volume), pectoral implants are less well known as to how to choose them for each patient. While the footprint of the pectoralis major muscle serves as the base outline of the implant, the concept of projection and volume is not as clear. How much muscular enhancement/projection is needed for any given patient as this will ultimately determine their perception of size.
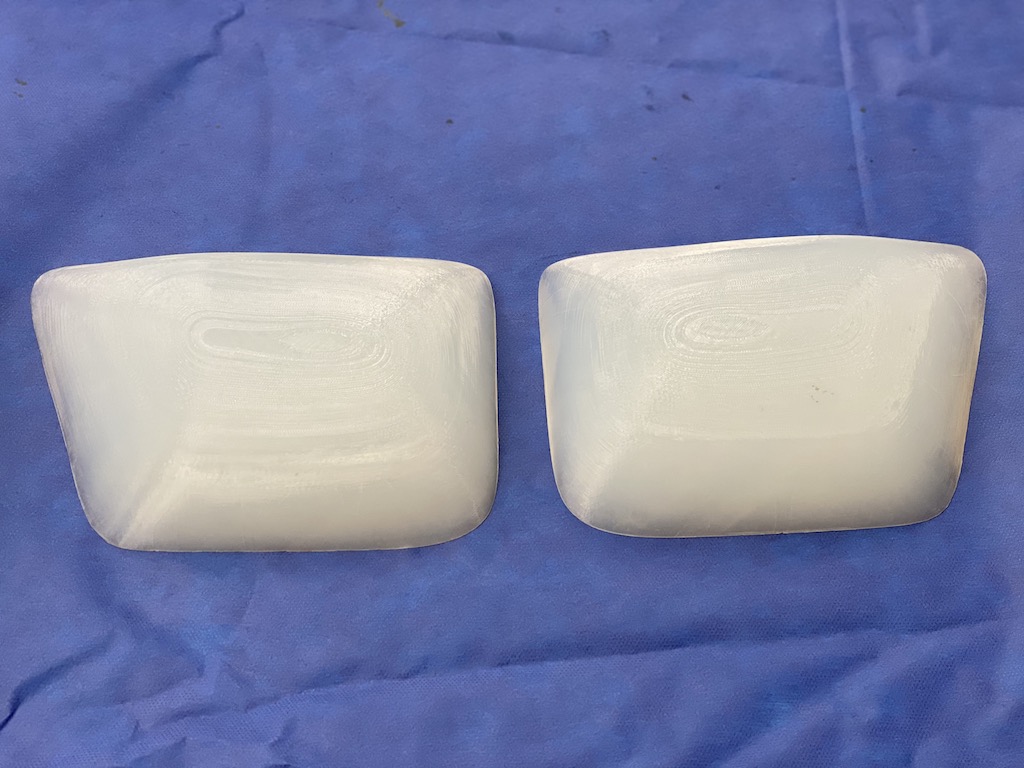
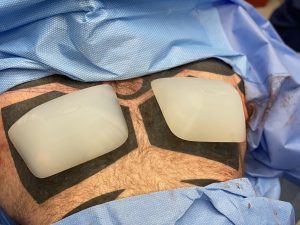
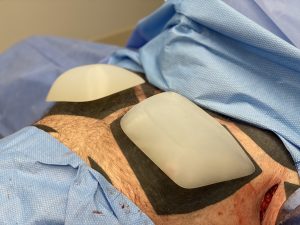
Pectoral implants, unlike breast implants, are not usually perceived in volume. (ccs) But there are some volumetric similarities with the understanding that men are generally a bit bigger than women. Most typical breast implant volumes are in the 250cc to 400cc range. A large breast augmentation for an average sized women would be in the 400 to 600cc range, extra large up to 800cc and an ‘extreme’ side anything over 800cc to 1000ccs. For men most pectoral implant volumes are in the 300 to 400cc range. Large pectoral implants are up to 650cc as this is the largest standard size. Anything pectoral implant volume that requires a custom implant design is usually greater than 700ccs.

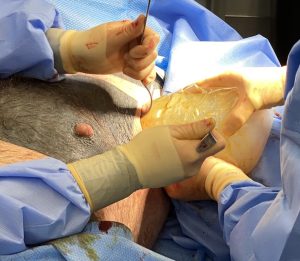

In any pectoral implant placement it is critical to not violate the inferior muscle attachments. This keeps the implant volume high well above the inferior nipple position. Usually in more common implant sizes the lateral pectoral border is not released. But in large pectoral implants as in this case it is necessary to do so to accommodate the implant’s size. In designing a custom implant the projection can be very similar across the implant’s projection, only tapering it slightly at all edges. This ensures a maximum and uniform projection throughout the external chest contour.
Case Highlights:
1) XL pectoral implants typically have volumes that exceed 650ccs.
2) The axillary incision needed to place larger pectoral implants does not need to be much bigger than more typical implant sizes.
3) Getting a larger pectoral implant through the axillary incision is accomplished by a combination of a low durometer solid silicone and a funnel insertion device.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana