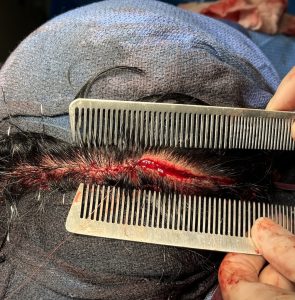
Background: The aesthetically wide head is typically seen as a pronounced convexity in the temporal regions of the skull. While much of the skull is compromised of bone under the scalp, the temporal regions which make up the sides of the head are unique in that regard. While there is temporal bone a significant part of its thickness is muscle. The muscle thickness can vary from person tom person as well as amongst different ethnicities. But it is fair to say in my experience that it is at least 50% of the width for most people. As a result the wide head and the convexity seen has a major component of muscle to it. Successful management of the wide head therefore has to have a strategy for muscle thinning. (temporal reduction)
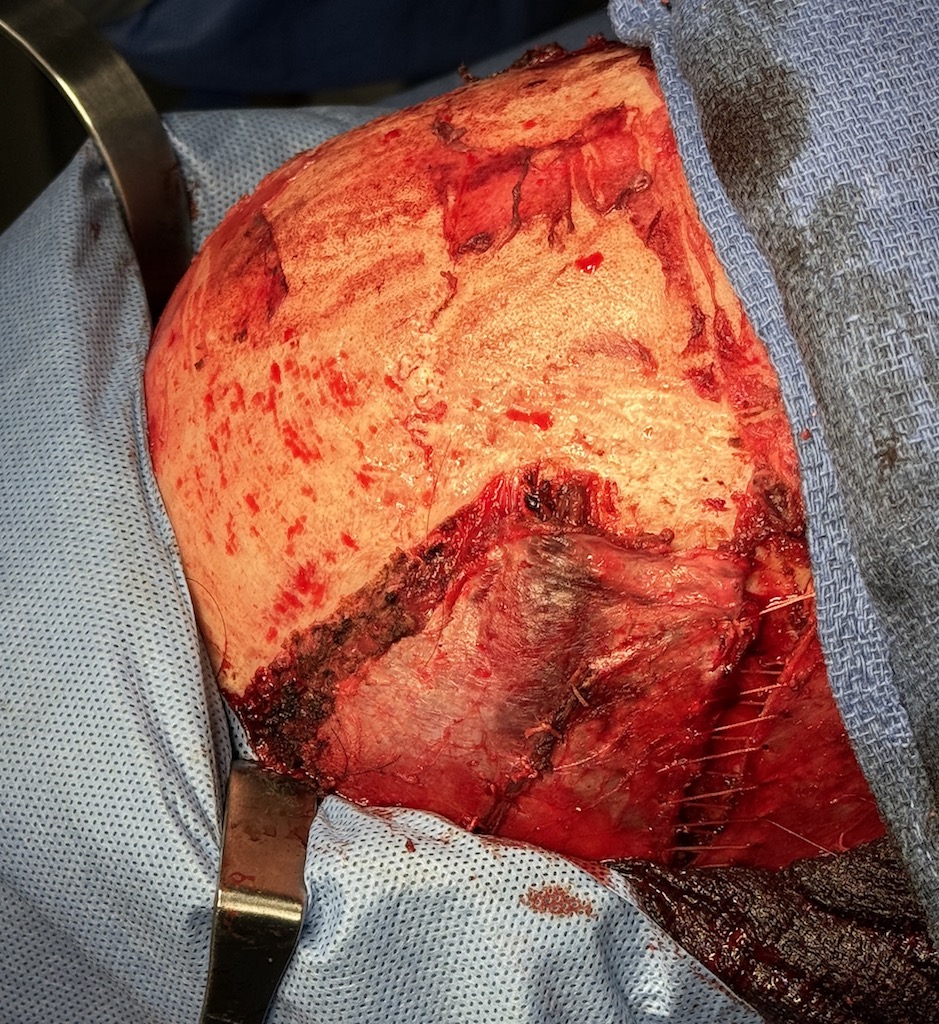
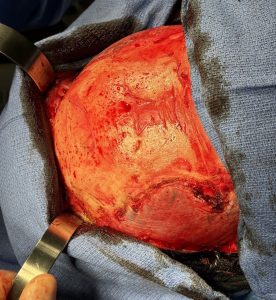
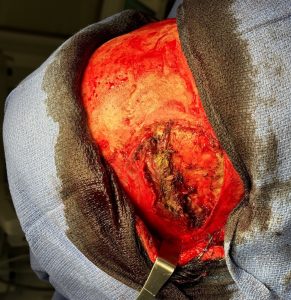
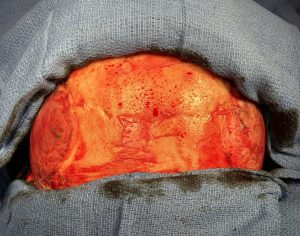
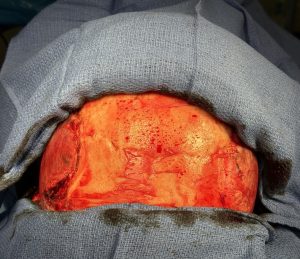
When it comes to temporal (head widening) reduction there are 4 types. Posterior temporal muscle excision (Type 1) and posterior temporal muscle excision with anterior temporal muscle transposition (Type 2) are performed through a hidden scar behind the ears. (postauricular sulcus) Type 3 temporal reduction uses an incision along the sides of the head for posterior temporal muscle excision, anterior temporal muscle transposition as well as temporal bone burring reduction. Type 4 is the maximal head widening procedure in which every component is addressed to the maximum with posterior temporal muscle excision, anterior temporal muscle release with mid-wedge excision as well as lateral bony forehead/temporal line and temporal bone burring reductions. This maximal head widening approach is done through a transcoronal scalp incision.

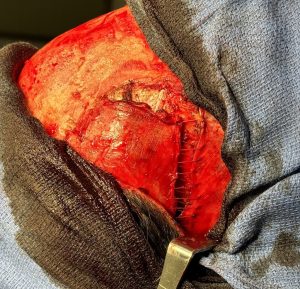
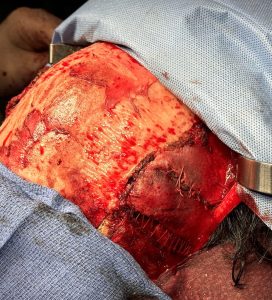
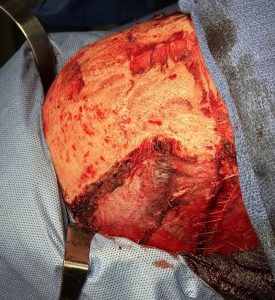
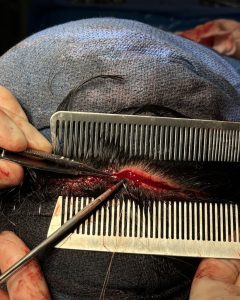
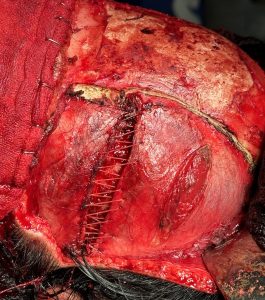
Over drains the scalp was closed in two layers (fascia and skin) using a double comb technique to meticulously put together the top scalp layer with fine 5-0 plain sutures.
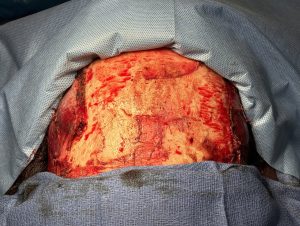
While a type 4 temporal reduction achieves maximal head width by muscle and bone manipulations the aesthetic tradeoff is the scalp scar. Whether the transcoronal scalp scar is worthy of the most that can be achieved in head width reduction surgery is an individual patient decision. Suffice it to say that such an aesthetic tradeoff is likely more acceptable in a patient with hair.
Highlights:
- A very wide head is the result of large temporal muscle hypertrophy and associated widening of the bony forehead and temporal lines.
- Type 4 temporal (head) reduction employs wide open access using a transcoronal incision for both muscle and bony reductions.
- Despite the severity of its appearance the type 4 temporal reduction is not associated with substantial more swelling or recovery than Types 1 – 3.
Dr. Barry Eppley
World-Renowned Plastic Surgeon