Background: The forehead occupies up to one-third of the face and is largely devoid of many discerning features. Short of the eyebrows/brow bones at its lower end, the characteristics of the forehead are mainly influenced by the aging effects of the overlying skin (wrinkles) and the location of the frontal and temporal hairlines.
The large bony surface of the forehead is generally smooth with varying degrees of convexity. The unique characteristic of the forehead is that its large curved bony surface is exposed to lighting from every angle. As a result every surface feature becomes apparent and even small high and low spots are easily discernible.
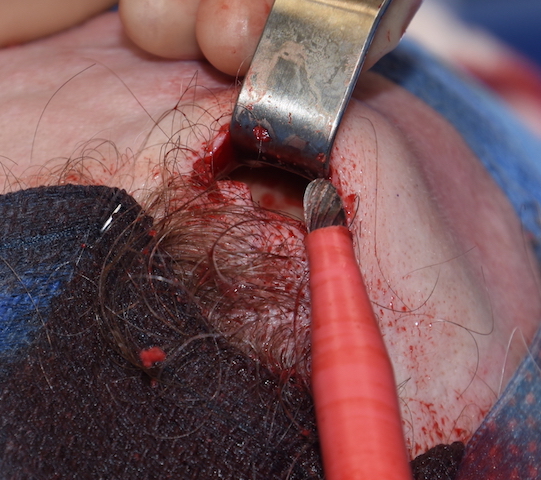
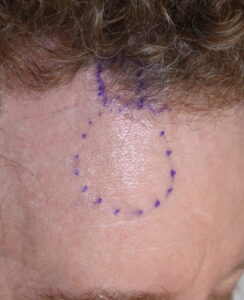
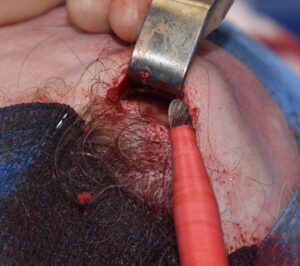
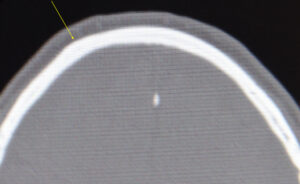
Such is the case with the frontal eminences also known as forehead horns. These solitary or paired small bony prominences appear as raised bumps at the upper third of the forehead. Their actual amount of surface elevation is often quite small (a few millimeters) but yet they can be quite visible. Patients particularly mention of their visibility in certain lighting.
Case Highlights:
1) Frontal eminence (forehead horn) reduction is associated with a modest increase in bone thickness in a circular pattern.
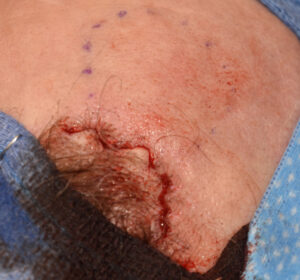
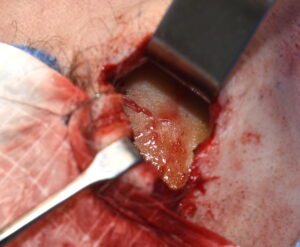
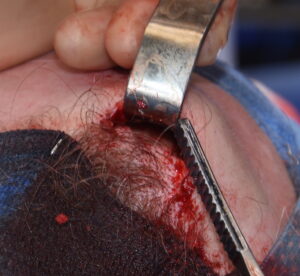
2) These small spot forehead reductions are done by a bone burring technique through a direct overlying hairline or scalp incision.
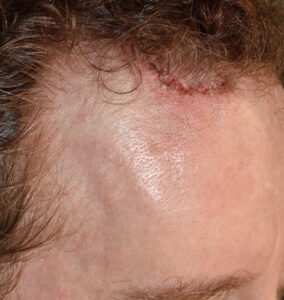
3) Recurrence of frontal eminence reductions is not a postoperative occurrence I have seen.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana