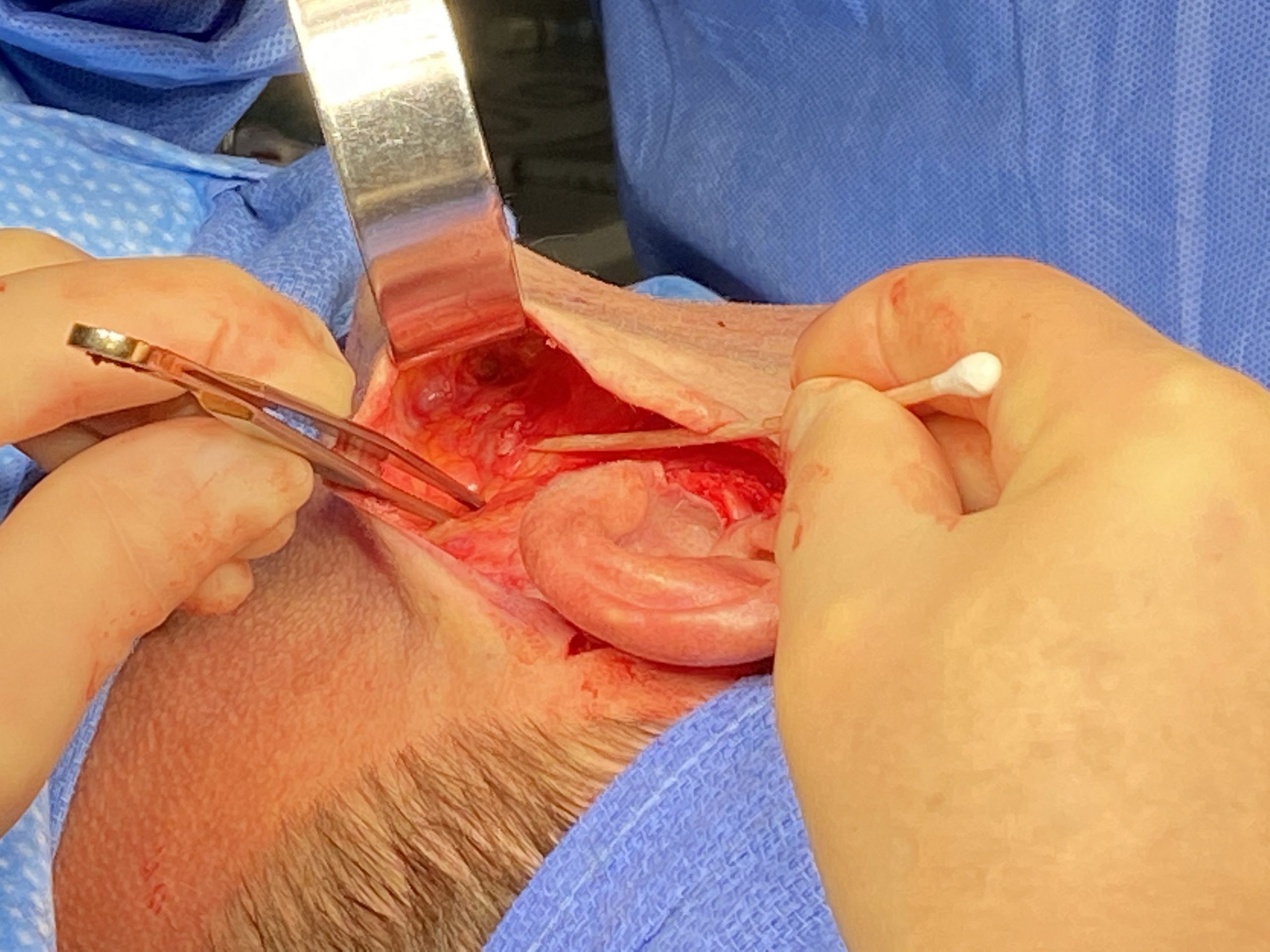
In the June 2021 issue of the journal Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery an article was published on this topic entitled ‘Perioperative Approach to Reducing Hematoma during Rhytidectomy: What Does the Evidence Show?’ In this paper the authors review which measures to prevent hematoma formation after facelift surgery are supported by the medical evidence in published studies. In doing so they review articles that were published on the subject over a forty-five year period from 1975 to 2020. (2,391 articles) The highlights of their findings are as follows:
Perioperative blood pressure control has been a critical element of undergoing facelift surgery for a long time. The antihypertension regime used is critical and it is important to not use intraop hypotension and avoid post rebound hypertension where the systolic pressure exceeds 140mm. The anesthesia used plays a major role if a smooth induction and emergence (no bucking) and the post nausea and vomiting is avoided.
Preinfiltration of the tissues to be undermined and elevated is a uniform maneuver in facelift surgery. What has become more popular recently is a tumescent type of infiltration somewhat analogous to that used in liposuction. There is no uniformly used infiltrate preparation that has been shown to be superior in preventing hematoma formation. Whether this is an essential remain remains unclear but its ancillary benefits of the hydrodissection and decreased postoperative bruising will continue to make its use popular amongst some facelift surgeons.
The evidence does not support that either PRP (platelet-rich plasma) or fibrin tissue sealants reduce facelift hematomas. They do have their benefits in reducing seroma/drain rates, bruising and post swelling but just not specifically in prevention of hematoma.
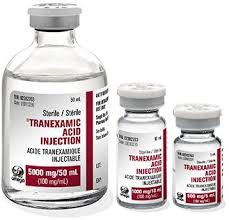
This paper provides a current medically based review of the proven methods of preventing hematomas in facelift surgery. Perioperative blood pressure control, the anesthetic choice and its execution, preinfiltration and the use of tranexamic acid appear to be formidable in their effects which are maximized when combined as a comprehensive strategy.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana