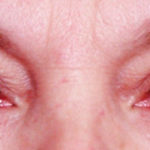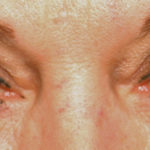
The corrugator supercilii are small paired muscles with a pyramidal shape which are located along inner edge of the brow bones at the nose. They are located beneath the overlying orbicularis oculii and frontalis muscle but do send fibers that pass through them to attach to the underside of the skin. An understanding of this anatomy has lead to their surgical treatment through a direct or upper eyelid incision for their resection leading to elevation of the medial brow and reduction of glabellar frown lines. This direct muscle resection approach also come in useful in the surgical treatment of frontal migraines.
In the February 2017 issue of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, a paper was published entitled ‘Transpalpebral Corrugator Resection: 25-Year Experience, Refinements and Additional Indications’. In this paper the senior author discusses his experience and expanded techniques from the transpalpebral corrugated muscle resection technique that he introduced in the early 1990s. He lists the modifications of his eyelid approach as follows: 1) a thin layer of depressor supercilii muscle is removed to expose the corrugator supercilii muscle, 2) a medial branch of the supraorbital nerve is used to trace a path through the muscle down to the periosteum, 3) a portion of the muscle lateral to the nerve is removed, 4) a superior segment of the muscle is removed by electrocautery, 5) a lateral segment of the procerus muscle is also removed, 6) for migraine surgery the supratrochlear and supraorbital arteries are cauterized as well as a foraminotomy if the nerve is fully encased by bone, and 7) fat injections are done to restore lost volume from the tissue resections.
The small size of the corrugator supercilii muscle and the limited access of the upper eyelid incision mandate a precise surgical technique for its resection if it is to be effective. Such refinements in the technique has described by this paper have led to improved results and addtionalk indications for its use.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana