Background: The scrotal sac normally contains two testicles. Loss of one of the testicles can occur from a variety of medical conditions from an undescended testes, infection and cancer removal to name a few. Generally, having only one testicle does not affect one’s testosterone levels or the ability to have children. But it does affect the appearance of the scrotal sac and one’s self-esteem.
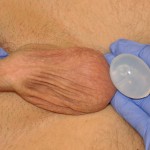
A lost testicle can be replaced by an implant and have been done so for over seventy years. Initially implants were composed metal, glass, plastic and even foam materials. But the first really successful testicle implants were placed in the 1970s and were composed of silicone gel-filled prosthesis not unlike that of breast implants. But with the breast implant fiasco that was initiated in 1991, silicone gel-filled testicular implants became unavailable. This led to the development and eventual FDA approval of a saline-filled testicular implant (with an outer silicone shell) that is widely used today.
Like is now known with breast implants, the use of silicone testicular implants has never been associated with the development of autoimmune or any other disorders. Unlike breast implants, however, todays solid silicone devices that can be used for testicular implants are not gel-filled but are a soft solid elastomer. Thus they can not leak or rupture and will never break down or need to be replaced because of material failure.
Case Study: This 30 year-old male had an undescended testicle removed as a child. He desired an implant so that he would once again have two testicles and better scrotal sac asymmetry.
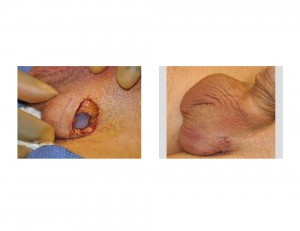
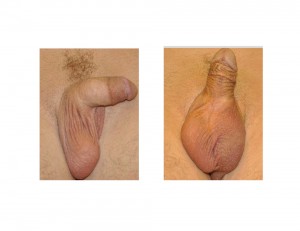
Testicular restoration by implants can be done successfully using FDA-approved saline-filled or off label solid silicone devices. Solid silicone has the advantage of being more economical and will not ever need to be replaced due to material failure by leakage or los of shell integrity.
Case Highlights:
1) Loss of a testicle creates scrotal asymmetry and may adversely affect a man’s self-image.
2) Testicular implant surgery is a simple and effective procedure that helps restore the scrotal appearance and feels natural.
3) Testicle implants are available in either saline-filled or soft silicone elastomer types.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana