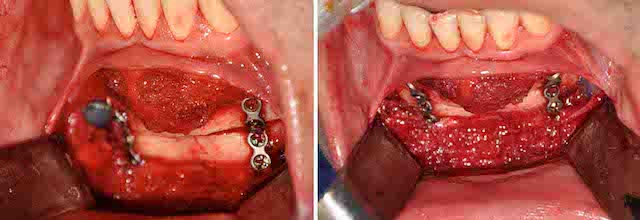
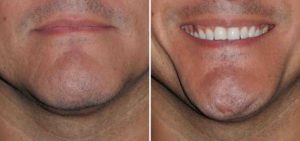
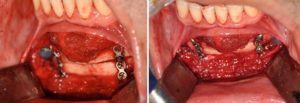
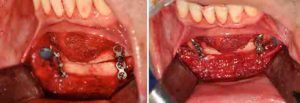
Background: Macrogenia is a generic term that refers to a large chin. But large chins come in a wide variety of shapes and dimensional excesses which do not respond to a single type of chin reduction surgery. It becomes important therefore to assess each case of macrogenia individually to determine its tissue composition for which the proper tissue reduction techniques can be applied.
Chin reduction surgery is far more commonly performed in women than men. While chin augmentation is equally performed amongst men and women, chin reduction is dominated by females. But regardless of the patient’s gender successful chin reduction surgery frequently involves a combination of both bone and soft tissue removals. Chin reduction is often erroneously perceived to be a bone reduction only procedure. This occurs due to a misdiagnosis of the problem as well as greater comfort with managing bone than the enveloping soft tissue chin pad.
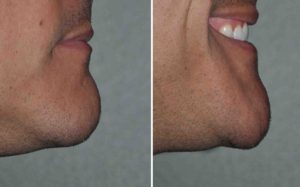
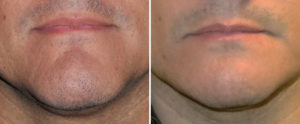
When assessing the large chin it is important to assess it in both static and smiling positions. The contribution of the soft tissue component, if any, of the large chin will become apparent when smiling as a chin pad ptosis occurs. If a dynamic chin pad ptosis is present and a bone reduction only approach is used the soft tissue excess will get worse and the large chin will not be satisfactorily reduced.

Case Highlights:
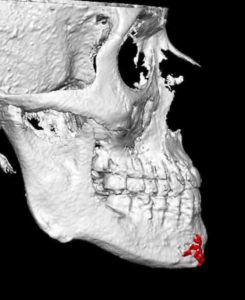
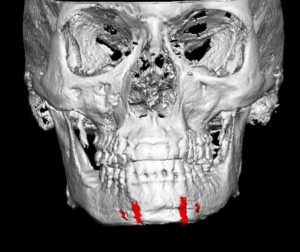
1) Large chins can be the result of excessive bone, a large soft tissue pad or both.
2) Many chin reductions require a combination of both bone and soft tissue reduction techniques.
3) The lateral prejowl implant adds width to a vertical chin reduction to achieve a smoother jawline behind the chin.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana