1. What is body implant surgery?
While everyone has heard of breast implants, few are aware that there are other locations for the placement of implants to enhance the contours of one’s body. All of these body implants are for the purposes of enhancing certain muscles. Think of body implants as muscle contouring surgery. These include traditional areas of the chest, buttocks, and calfs as well as newer implants for the arm (biceps and triceps), hip and deltoid areas. The majority of body implant patients are male.
Some may think that the use of these implants is cheating, as opposed to muscle growth through working out, but many of these procedures are used for reconstructive purposes as well. Some patients may use them to help with genetic or injury-related body deformities caused by such conditions as pectus excavatum, spina bifida, and clubfoot. These cause deformities marked by muscle atrophy, underdevelopment or asymmetry.
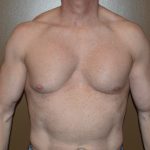
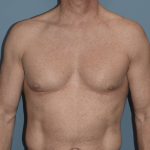
Yes and no. Pectoral implants, commonly referred to as breast implants for men or male chest implants, is done to enhance the appearance, size and outlines of the pectoral muscles. Like breast implants, they are very effective at creating that change and are associated with no greater amount of risks or complications. From the standpoint of location under the existing pectoralis muscle, they are very similar to breast implants in that regard.
They do differ in that the end goals are not the same. Breast implants are trying to make a rounded or tear-drop mound that sits up and away from the chest wall and has some compressibility. Pectoral implants are only trying to push out the existing muscle and, as a result, need less volume to do so. A muscle also has more of a firm feel to it rather than displacement to the touch like a breast. Therefore, pectoral implants are smaller in size and are composed of a soft but solid silicone elastomer. They are not fluid or gel-filled like breast implants.
3. What is the best way to achieve a larger and rounder buttocks?
There has been a significant increase in the number of buttock enlargement/enhancement requests. Fueled by increasing multiracial population growth and popular figures like Jennifer Lopez, more women are pursing an increased curvature to the buttocks through different forms of augmentation.
The debate in buttock augmentation is whether to do it through the use of an implant or with fat injections. There are surgeon advocates for both procedures and, when done well, satisfying results can be achieved either way. This is why it is important to look at each one’s advantages and disadvantages.
Buttock or gluteal implants have the advantages of a bigger and immediate result that will not change after surgery. Its downside is that it is a more invasive procedure, takes a lot longer to recover, and runs the risk of infection and implant displacement.
Fat injections have the advantage of a more ‘natural’ procedure that is not associated with any of the potential complications related to a foreign body. It also gives one the extra benefit of fat reduction from the donor site. Its disadvantages are that it can not usually achieve the same buttock size as that of an implant (at least in one fat grafting session) and the take of the fat graft is not completely predictable.
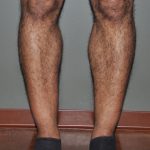
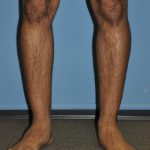
Calf augmentation creates fullness in the gastrocnemius muscle of the lower leg by placing implants in subfascial pockets overlying the muscle. It can help those men and women who can’t achieve the size of the calf muscle they desire. The calf muscle is one of the more difficult muscles in the body to enlarge due to its very compact muscle fibers. This form of lower leg sculpting can also correct muscle imbalance as a result of such congenital defects as disproportionate calf development, clubfoot, bowleggedness, and just plain skinny calfs. (aka ‘chicken legs’)
The calf muscle is a two-headed muscle in which one or two implants which may be used in each leg. A person may desire to have only the inner head of the muscle enlarged, the outer head, or both. They are inserted through a small incision in the skin crease behind the knee.
The biggest issue with calf implants is the recovery period. Because they are in the lower part of the legs, some significant swelling can occur. And it usually takes up to three weeks before one can walk more normally. Working out and other unrestricted activities will take at least a month or two following surgery.
Recent reports have seen the use of fat injections for calf augmentation. But this approach is just in its infancy and consistent long-term outcomes remain to be seen.
5. I have heard there are implants for the arms. Is this true?
Bicep and tricep implants will create muscular definition and perceived enlargement of the muscles in both the front and back of the upper arms. This procedure is done exclusively for those who can’t achieve the upper arm size they want even after significant efforts at muscular exercise. Generally, two implants are placed in each arm to give the greatest overall change.
6. Are there any new areas where body implants are being used?
The newest uses of body implants are for the hip and deltoid areas. Deltoid implants are used to rebuild or augment deficiencies of the deltoid muscle group caused by congenital deformities (Sprengel’s deformity or scapular hypoplasia) or traumatic injuries. (motor vehicle accidents) Hip implants are exclusively done for cosmetic augmentation. For those women who feel that their hips are too narrow and want more of an hourglass figure, hip implants can give them more curvature.
7. What complications can occur with body implants?
Placing an implant always has the standard medical risks of infection, displacement, and chronic pain as well as the cosmetic risks of over- or undercorrection. Unlike the face, body implants are always placed in areas exposed to constant motion and stress and are much larger in size. As a result, they have a higher incidence of fluid collections and displacement.
Dr. Barry Eppley
Indianapolis, Indiana